Question
The direction cosines of the projection of the line $$\frac{x}{{ - 2}} = \frac{{y - 1}}{1} = \frac{{z + 1}}{{ - 1}}$$ on the plane $$2x + y - 3z = 5$$ are :
A.
$$2,\, - 1,\,1$$
B.
$$\frac{2}{7},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{7},\,\frac{1}{7}$$
C.
$$\frac{{ - 2}}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{{\sqrt 6 }}$$
D.
$$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}$$
Solution :
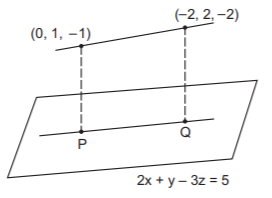
$$\eqalign{ & {\text{Let }}P = \left( {\alpha ,\,\beta ,\,\gamma } \right). \cr & {\text{Then }}2\alpha + \beta - 3\gamma = 5.....(1) \cr & {\text{and }}\frac{{\alpha - 0}}{2} = \frac{{\beta - 1}}{2} = \frac{{\gamma + 1}}{{ - 3}}......(2) \cr & {\text{Solving (1) and (2),}}\,\alpha = \frac{1}{7},\,\beta = \frac{{15}}{{14}},\,\gamma = \frac{{ - 17}}{{14}} \cr & {\text{Let }}Q = \left( {\alpha ',\,\beta ',\,\gamma '} \right). \cr & {\text{Then }}2\alpha ' + \beta ' - 3\gamma ' = 5.....(3) \cr & {\text{and }}\frac{{\alpha ' + 2}}{2} = \frac{{\beta ' - 2}}{1} = \frac{{\gamma ' + 2}}{{ - 3}}......(4) \cr & {\text{Solving (3) and (4),}}\,\alpha ' = \frac{{ - 13}}{7},\,\beta ' = \frac{{29}}{{14}},\,\gamma ' = \frac{{ - 31}}{{14}} \cr} $$
$$\therefore $$ direction ratios of $$PQ$$ are $$\frac{1}{7} - \left( { - \frac{{13}}{7}} \right),\,\frac{{15}}{{14}} - \frac{{29}}{{14}},\,\frac{{ - 17}}{{14}} - \left( {\frac{{ - 31}}{{14}}} \right)$$ i.e., $$2,\, - 1,\,1.$$ So, direction cosines are $$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}.$$

$$\eqalign{ & {\text{Let }}P = \left( {\alpha ,\,\beta ,\,\gamma } \right). \cr & {\text{Then }}2\alpha + \beta - 3\gamma = 5.....(1) \cr & {\text{and }}\frac{{\alpha - 0}}{2} = \frac{{\beta - 1}}{2} = \frac{{\gamma + 1}}{{ - 3}}......(2) \cr & {\text{Solving (1) and (2),}}\,\alpha = \frac{1}{7},\,\beta = \frac{{15}}{{14}},\,\gamma = \frac{{ - 17}}{{14}} \cr & {\text{Let }}Q = \left( {\alpha ',\,\beta ',\,\gamma '} \right). \cr & {\text{Then }}2\alpha ' + \beta ' - 3\gamma ' = 5.....(3) \cr & {\text{and }}\frac{{\alpha ' + 2}}{2} = \frac{{\beta ' - 2}}{1} = \frac{{\gamma ' + 2}}{{ - 3}}......(4) \cr & {\text{Solving (3) and (4),}}\,\alpha ' = \frac{{ - 13}}{7},\,\beta ' = \frac{{29}}{{14}},\,\gamma ' = \frac{{ - 31}}{{14}} \cr} $$
$$\therefore $$ direction ratios of $$PQ$$ are $$\frac{1}{7} - \left( { - \frac{{13}}{7}} \right),\,\frac{{15}}{{14}} - \frac{{29}}{{14}},\,\frac{{ - 17}}{{14}} - \left( {\frac{{ - 31}}{{14}}} \right)$$ i.e., $$2,\, - 1,\,1.$$ So, direction cosines are $$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{{ - 1}}{{\sqrt 6 }},\,\frac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}.$$