Question
If $$OABC$$ is a tetrahedron where $$O$$ is the origin and $$A,\,B,\,C$$ are three other vertices with position vectors $$\overrightarrow a ,\,\overrightarrow b $$ and $$\overrightarrow c $$ respectively, then the centre of sphere circumscribing the tetrahedron is given by the position vector :
A.
$$\frac{{{a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}$$
B.
$$\frac{{{b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}$$
C.
$$\frac{{{b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}$$
D.
$$\frac{{{a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right) + {b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{{a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}$$
Solution :
If the centre $$'P'$$ is with position vector $$\overrightarrow r ,$$
Then $$\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PA} ,\,\overrightarrow b - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PB} ,\,\overrightarrow c - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PC} ,$$
Where $$\left| {\overrightarrow {PA} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {PB} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {PC} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {OP} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow r } \right|$$
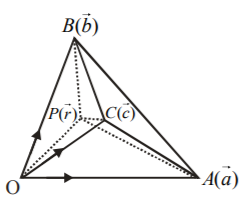
$$\eqalign{ & {\text{Consider }}\left| {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow r } \right| \cr & \Rightarrow \left( {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right).\left( {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right) = \overrightarrow r .\overrightarrow r \cr & \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r + {r^2} = {r^2} \cr & \Rightarrow {a^2} = 2\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r \cr & {\text{Similarly, }}{b^2} = 2\overrightarrow b .\overrightarrow r {\text{ and }}{c^2} = 2\overrightarrow c .\overrightarrow r \cr & {\text{Since, }}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right),\,\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right){\text{ and }}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right){\text{ are non - coplanar,}} \cr & {\text{then }}\overrightarrow r = x\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + y\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + z\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right) \cr & \Rightarrow \overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r = x\overrightarrow a .\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + y.0 + z.0 \cr & \Rightarrow \overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r = x\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right] \cr & \Rightarrow x = \frac{{\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r }}{{\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & \Rightarrow x = \frac{{{a^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & {\text{Similarly, }}y = \frac{{{b^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}{\text{ and }}z = \frac{{{c^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & {\text{Therefore, }}\overrightarrow r = \frac{{{a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr} $$
If the centre $$'P'$$ is with position vector $$\overrightarrow r ,$$
Then $$\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PA} ,\,\overrightarrow b - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PB} ,\,\overrightarrow c - \overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {PC} ,$$
Where $$\left| {\overrightarrow {PA} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {PB} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {PC} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {OP} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow r } \right|$$

$$\eqalign{ & {\text{Consider }}\left| {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow r } \right| \cr & \Rightarrow \left( {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right).\left( {\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow r } \right) = \overrightarrow r .\overrightarrow r \cr & \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r + {r^2} = {r^2} \cr & \Rightarrow {a^2} = 2\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r \cr & {\text{Similarly, }}{b^2} = 2\overrightarrow b .\overrightarrow r {\text{ and }}{c^2} = 2\overrightarrow c .\overrightarrow r \cr & {\text{Since, }}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right),\,\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right){\text{ and }}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right){\text{ are non - coplanar,}} \cr & {\text{then }}\overrightarrow r = x\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + y\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + z\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right) \cr & \Rightarrow \overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r = x\overrightarrow a .\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + y.0 + z.0 \cr & \Rightarrow \overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r = x\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right] \cr & \Rightarrow x = \frac{{\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r }}{{\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & \Rightarrow x = \frac{{{a^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & {\text{Similarly, }}y = \frac{{{b^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}}{\text{ and }}z = \frac{{{c^2}}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr & {\text{Therefore, }}\overrightarrow r = \frac{{{a^2}\left( {\overrightarrow b \times \overrightarrow c } \right) + {b^2}\left( {\overrightarrow c \times \overrightarrow a } \right) + {c^2}\left( {\overrightarrow a \times \overrightarrow b } \right)}}{{2\left[ {\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b \overrightarrow c } \right]}} \cr} $$