Question
Consider the function, $$f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| + \left| {x - 5} \right|,\,x \in \,R.$$
Consider the function, $$f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| + \left| {x - 5} \right|,\,x \in \,R.$$
Statement-1 : $$f'\left( 4 \right) = 0$$
Statement-2 : $$f$$ is continuous in [2, 5], differentiable in (2, 5) and $$f\left( 2 \right) = f\left( 5 \right).$$
A.
Statement-1 is false, Statement-2 is true.
B.
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true; statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
C.
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
D.
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false.
Answer :
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Solution :
\[\begin{array}{l} f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 2\,\,,\,\,x - 2 \ge 0\\ 2 - x\,\,,\,\,x - 2 \le 0 \end{array} \right.\\ = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 2\,\,,\,\,x \ge 2\\ 2 - x\,\,,\,\,x \le 2 \end{array} \right. \end{array}\]
Similarly, \[f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 5} \right| = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 5\,\,,\,\,x \ge 5\\ 5 - x\,\,,\,\,x \le 5 \end{array} \right.\]
$$\eqalign{ & \therefore f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| + \left| {x - 5} \right| \cr & = \left\{ {x - 2 + 5 - x = 3,\,\,2 \leqslant x \leqslant 5} \right\} \cr & {\text{Thus}} \cr & f\left( x \right) = 3,\,2 \leqslant x \leqslant 5 \cr & f'\left( x \right) = 0,\,2 < x < 5 \cr & f'\left( 4 \right) = 0 \cr} $$
$$\therefore $$ statement 1 is true.
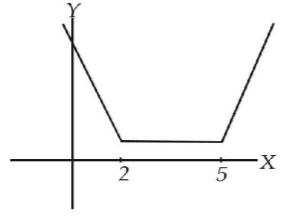
$$\because f\left( 2 \right) = 0 + \left| {2 - 5} \right| = 3$$ and $$f\left( 5 \right) = \left| {5 - 2} \right| + 0 = 3$$
$$\therefore $$ statement-2 is also true and a correct explanation for statement 1.
\[\begin{array}{l} f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 2\,\,,\,\,x - 2 \ge 0\\ 2 - x\,\,,\,\,x - 2 \le 0 \end{array} \right.\\ = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 2\,\,,\,\,x \ge 2\\ 2 - x\,\,,\,\,x \le 2 \end{array} \right. \end{array}\]
Similarly, \[f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 5} \right| = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - 5\,\,,\,\,x \ge 5\\ 5 - x\,\,,\,\,x \le 5 \end{array} \right.\]
$$\eqalign{ & \therefore f\left( x \right) = \left| {x - 2} \right| + \left| {x - 5} \right| \cr & = \left\{ {x - 2 + 5 - x = 3,\,\,2 \leqslant x \leqslant 5} \right\} \cr & {\text{Thus}} \cr & f\left( x \right) = 3,\,2 \leqslant x \leqslant 5 \cr & f'\left( x \right) = 0,\,2 < x < 5 \cr & f'\left( 4 \right) = 0 \cr} $$
$$\therefore $$ statement 1 is true.

$$\because f\left( 2 \right) = 0 + \left| {2 - 5} \right| = 3$$ and $$f\left( 5 \right) = \left| {5 - 2} \right| + 0 = 3$$
$$\therefore $$ statement-2 is also true and a correct explanation for statement 1.