41.
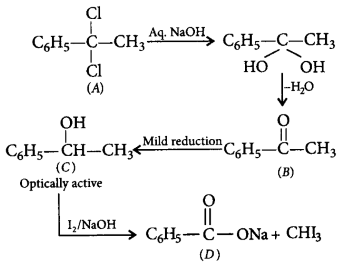
\[{{C}_{8}}{{H}_{8}}C{{l}_{2}}\left( A \right)\xrightarrow{Aq.\,NaOH}\left( B \right)\] \[\xrightarrow{\text{Mild reduction}}\left( C \right)\xrightarrow{\frac{{{I}_{2}}}{NaOH}}\] \[\text{iodoform + acid salt }\left( D \right)\]
In the given sequence of reaction, what would be the structure of $$(A)?$$
A
$$PhCOC{H_3}$$
B
$$PhCH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3}$$
C
$$PhCOONa$$
D
$$PhC{\left( {Cl} \right)_2}C{H_3}$$
Answer :
$$PhC{\left( {Cl} \right)_2}C{H_3}$$
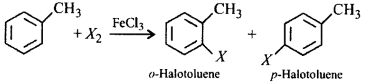
42. Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving $$ortho$$ and $$para$$ halo compounds. The reaction is
A
electrophilic elimination reaction
B
electrophilic substitution reaction
C
free radical addition reaction
D
nucleophilic substitution reaction
Answer :
electrophilic substitution reaction
43. $$36.4\,g$$ of 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrachloropropane was heated with zinc dust and the product was bubbled through ammoniacal $$AgN{O_3}.$$ What is the weight of precipitate obtained?
A
30.0 $$g$$
B
29.4 $$g$$
C
28.0 $$g$$
D
25.7 $$g$$
Answer :
29.4 $$g$$
44. Triiodomethane has antiseptic property because of
A
liberation of iodoform
B
liberation of free iodine
C
formation of phosgene gas
D
none of these
Answer :
liberation of free iodine
45. Butane nitrile can be prepared by heating
A
propyl alcohol with $$KCN$$
B
butyl chloride with $$KCN$$
C
butyl alcohol with $$KCN$$
D
propyl chloride with $$KCN$$
Answer :
propyl chloride with $$KCN$$
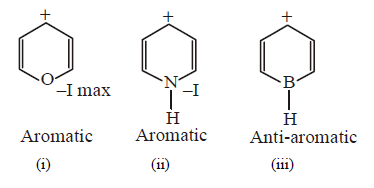
47.
Identify correct reactivity order for $${S_N}1$$ reaction
A
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
B
(ii) > (iii) > (i)
C
(i) > (iii) > (ii)
D
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
Answer :
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
48. Pure chloroform is prepared by
A
distilling chloral hydrate with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
B
heating ethanol with bleaching powder.
C
heating acetone with bleaching powder.
D
reducing carbon tetrachloride.
Answer :
distilling chloral hydrate with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
49. Identify $$Z$$ in \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Br\xrightarrow{aq.\,NaOH}X\] \[\xrightarrow{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}Y\xrightarrow{C{{l}_{2}}/{{H}_{2}}O}Z\]
A
$${\text{Mixture of}}\,C{H_3}CHClC{H_2}Cl$$ $${\text{and}}\,\,C{H_3}CHOHC{H_2}Cl$$
B
$$C{H_3}CHOHC{H_2}Cl$$
C
$$C{H_3}CHClC{H_2}OH$$
D
$$C{H_3}CHClC{H_2}Cl$$
Answer :
$$C{H_3}CHOHC{H_2}Cl$$
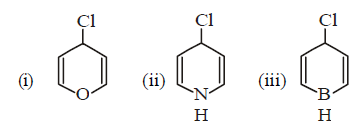
50.
Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of $$623\,K$$ and a pressure of $$300\,atm.$$ However the rate of reaction can be increased by presence of certain groups in benzene ring. What will be the order of reactivity of following compounds towards the above substitution reaction?
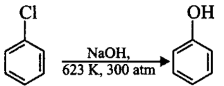
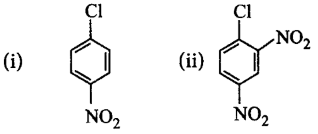
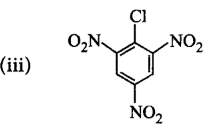
A
(iii) > (ii) > (i)
B
(ii) > (iii) > (i)
C
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
D
(i) > (iii) > (ii)
Answer :
(iii) > (ii) > (i)