141. The main difference in $$C - X$$ bond of a haloalkane and a haloarene is
A
$$C - X$$ bond in haloalkanes is shorter than haloarenes.
B
in haloalkanes the $$C$$ attached to halogen in $$C - X$$ bond is $$s{p^3}$$ hybridised while in haloarenes it is $$s{p^2}$$ hybridised.
C
$$C - X$$ bond in haloarenes acquires a double bond character due to higher electronegativity of $$X$$ than haloalkanes.
D
haloalkanes are less reactive than haloarenes due to difficulty in $$C - X$$ cleavagein haloalkanes.
Answer :
in haloalkanes the $$C$$ attached to halogen in $$C - X$$ bond is $$s{p^3}$$ hybridised while in haloarenes it is $$s{p^2}$$ hybridised.
142.
The following reaction proceeds through the intermediate formation of
$$RCOOAg + B{r_2} \to RBr + C{O_2} + AgBr$$
A
$$RCO{O^ \bullet }$$
B
$${R^ \bullet }$$
C
$$B{r^ \bullet }$$
D
$${\text{All of these}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{All of these}}$$
143.
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom$$(s)$$ attached to the $$s{p^3}$$ hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group. Identify haloalkane from the following compounds.
(i) 2-Bromopentane
(ii) Vinyl chloride
(iii) 2-Chloroacetophenone
(iv) Trichloromethane
A
(ii) only
B
Only (ii) and (iv)
C
Only (i) and (iv)
D
Only (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer :
Only (i) and (iv)
144.
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
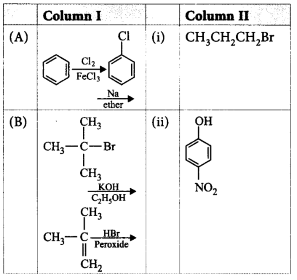

A
A - iv, B - ii, C - i, D - iii
B
A - iii, B - iv, C - ii, D - i
C
A - ii, B - i, C - iii, D - iv
D
A - i, B - iii, C - iv, D - ii
Answer :
A - iii, B - iv, C - ii, D - i
145.
Which is the correct increasing order of boiling points of the following compounds?
1-Iodobutane, 1-Bromobutane, 1-Chlorobutane, Butane
A
Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane
B
1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane < Butane
C
Butane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Chlorobutane
D
Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Iodobutane < 1-Bromobutane
Answer :
Butane < 1-Chlorobutane < 1-Bromobutane < 1-Iodobutane
146. Which of the following compounds can yield only one monochlorinated product upon free radical chlorination?
A
2, 2-Dimethylpropane
B
2-Methylpropane
C
2-Methylbutane
D
$$n$$ - Butane
Answer :
2, 2-Dimethylpropane
147. The Wurtz-Fittig reaction involves condensation of
A
two molecules of aryl halides.
B
one molecule of each of aryl-halide and alkyl-halide.
C
one molecule of each of aryl-halide and phenol.
D
two molecules of aralkyl-halides.
Answer :
one molecule of each of aryl-halide and alkyl-halide.
149. A mixture of 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane when treated with alcoholic $$KOH$$ gives
A
prop-1-ene
B
prop-2-ene
C
a mixture of prop-1-ene and prop-2-ene
D
propanol
Answer :
prop-1-ene
150. Which of the following reactions is not correctly matched?
A
\[2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}Br+2Na\xrightarrow{\text{dry}\,\,\text{ether}}\] \[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}+2NaBr\,;\,\text{Wurtz reaction }\]
B
\[C{{H}_{3}}Br+AgF\to C{{H}_{3}}F+AgBr\,;\] \[\text{Etard reaction }\]
C
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Br+2Na+Br{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow{\text{dry}\,\,\text{ether}}\] \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+2NaBr\,;\] \[\text{Wurtz-Fittig reaction}\]
D
\[2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}Br+2Na\xrightarrow{\text{dry}\,\,\text{ether}}\] \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}+2NaBr\,;\] \[\text{Fittig reaction}\]
Answer :
\[C{{H}_{3}}Br+AgF\to C{{H}_{3}}F+AgBr\,;\] \[\text{Etard reaction }\]






