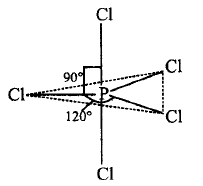
381. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the structure of $$PC{l_5}?$$
A
Three $$P - Cl$$ bonds lie in one plane and two $$P - Cl$$ bonds lie above and below the equatorial plane.
B
Five $$P - Cl$$ bonds lie in the same plane.
C
The bond angle in all $$P - Cl$$ bonds is $${90^ \circ }.$$
D
The bond length of all $$P - Cl$$ bonds is same.
Answer :
Three $$P - Cl$$ bonds lie in one plane and two $$P - Cl$$ bonds lie above and below the equatorial plane.
382. Which of the following does not apply to metallic bond ?
A
Overlapping valence orbitals
B
Mobile valency electrons
C
Delocalized electrons
D
Highly directed bonds.
Answer :
Highly directed bonds.
383. Which of the following statements is true about hydrogen bonding?
A
$$Cl$$ and $$N$$ have comparable electronegativities yet there is no $$H$$ - bonding in $$HCl$$ because size of $$Cl$$ is large.
B
Intermolecular $$H$$ - bonding results in decrease in $$m.pt.$$ and $$b.pt.$$
C
Ice has maximum density at $${0^ \circ }C$$ due to $$H$$ - bonding.
D
$$KHC{l_2}\left( {HCl_2^ - } \right)$$ exists but $$KH{F_2}\left( {HF_2^ - } \right)$$ does not exist due to lack of $$H$$ - bonding in $$HCl.$$
Answer :
$$Cl$$ and $$N$$ have comparable electronegativities yet there is no $$H$$ - bonding in $$HCl$$ because size of $$Cl$$ is large.
384. The number and type of bonds between two carbon atoms in $$Ca{C_2}$$ are:
A
one sigma $$\left( \sigma \right)$$ and one pi $$\left( \pi \right)$$ bonds
B
one sigma $$\left( \sigma \right)$$ and two pi $$\left( \pi \right)$$ bonds
C
one sigma $$\left( \sigma \right)$$ and one and a half pi $$\left( \pi \right)$$ bonds
D
one sigma $$\left( \sigma \right)$$ bond.
Answer :
one sigma $$\left( \sigma \right)$$ and two pi $$\left( \pi \right)$$ bonds