241.
Which of the following are arranged in an increasing order of their bond strengths? A
$$\,O_2^ - < {O_2} < O_2^ + < O_2^{2 - }$$
B
$$O_2^{2 - } < O_2^ - < {O_2} < O_2^ + $$
C
$$\,O_2^ - < O_2^{2 - } < {O_2} < O_2^ + $$
D
$$O_2^ + < {O_2} < O_2^ - < O_2^{2 - }$$
Answer :
$$O_2^{2 - } < O_2^ - < {O_2} < O_2^ + $$
View Solution
Discuss Question
$$\eqalign{
& O_2^ + \left( {15} \right) = KK\sigma 2{s^2},{\sigma ^*}2{s^2},\sigma 2p_x^2, \cr
& \left\{ {\pi 2p_y^2 = \pi 2p_z^2,\,\,\left\{ {{\pi ^*}2p_y^1 = \pi 2p_z^0} \right.} \right.\, \cr
& {\text{Bond}}\,{\text{order}}\, = \frac{1}{2}\left( {8 - 3} \right) = \frac{5}{2} = 2.5 \cr
& {O_2}\left( {16} \right) = KK\sigma 2{s^2},{\sigma ^*}2{s^2},\sigma 2p_x^2, \cr
& \left\{ {\pi 2p_y^2 = \pi 2p_z^2,\,\,\left\{ {{\pi ^*}2p_y^1 = {\pi ^*}2p_z^1} \right.} \right.\, \cr
& {\text{Bond}}\,{\text{order}}\, = \frac{1}{2}\left( {8 - 4} \right) = 2 \cr
& O_2^ - \left( {17} \right) = KK\sigma 2{s^2},\,{\sigma ^*}2{s^2},\sigma 2p_x^2, \cr
& \left\{ {\pi 2p_y^2 = \pi 2p_z^2,\,\,\left\{ {{\pi ^*}2p_y^2 = {\pi ^*}2p_z^1} \right.} \right. \cr
& {\text{Bond}}\,\,{\text{order}}\, = \frac{1}{2}\left( {8 - 5} \right) - 1.5 \cr
& O_2^{2 - }\left( {18} \right) = KK\sigma 2{s^2}{\sigma ^*}2{s^2}\sigma 2p_x^2, \cr
& \left\{ {\pi 2p_y^2 = \pi 2p_z^2,\,\,\left\{ {{\pi ^*}2p_y^2 = {\pi ^*}2p_z^2} \right.} \right. \cr
& {\text{Bond}}\,\,{\text{order}} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {8 - 6} \right) = 1 \cr} $$
242.
In which of the following sets, all the given species are isostructural ? A
$$C{O_2},N{O_2},Cl{O_2},Si{O_2}$$
B
$$PC{l_3},Al\,C{l_3},BC{l_3},SbC{l_3}$$
C
$$B{F_3},N{F_3},P{F_3},Al\,{F_3}$$
D
$$BF_4^ - ,CC{l_4},NH_4^ + ,PCl_4^ + $$
Answer :
$$BF_4^ - ,CC{l_4},NH_4^ + ,PCl_4^ + $$
243.
The species having bond order different from that in $$CO$$ IS A
$$N{O^ - }$$
B
$$N{O^{ + \,\,}}$$
C
$$C{N^ - }$$
D
$${N_2}$$
Answer :
$$N{O^ - }$$
View Solution
Discuss Question
Molecular electronic configuration of
244.
Which of the following statements is incorrect ? A
$$N{H_3}$$ is more basic than $$P{H_3}.$$
B
$$N{H_3}$$ has a higher boiling point than that of $$HF.$$
C
$${N_2}$$ is less reactive than $${P_4}.$$
D
The dipole moment of $$N{H_3}$$ is less than that of $$S{O_2}.$$
Answer :
$$N{H_3}$$ has a higher boiling point than that of $$HF.$$
View Solution
Discuss Question
Due to high $$EN$$ of $$F$$ than $$N, H$$ - bonding is stronger in $$HF$$ than $$N{H_3}$$ thus $$b.pt.$$ of $$HF > N{H_3}.$$
245.
Specify the coordination geometry around and hybridisation of $$N$$ and $$B$$ atoms in a $$1:1$$ complex of $$B{F_3}$$ and $$N{H_3}$$ A
$$N:$$ tetrahedral, $$s{p^3};B:$$ tetrahedral, $$s{p^3}$$
B
$$N:$$ pyramidal, $$s{p^3};B:$$ pyramidal, $$s{p^3}$$
C
$$N:$$ pyramidal, $$s{p^3};B:$$ planar, $$s{p^2}\,$$
D
$$N:$$ pyramidal, $$s{p^3};B:$$ tetrahedral, $$s{p^3}$$
Answer :
$$N:$$ tetrahedral, $$s{p^3};B:$$ tetrahedral, $$s{p^3}$$
View Solution
Discuss Question
$${H_3}N \to B{F_3}$$ where both $$N,B$$ are attaining tetrahedral geomerty.
246.
Which one among the following does not have the hydrogen bond? A
phenol
B
liquid $$N{H_3}$$
C
water
D
liquid $$HCl$$
Answer :
liquid $$HCl$$
View Solution
Discuss Question
TIPS/Formulae : Hydrogen bonding is formed in those compounds in which $$F$$ or $$O$$ or $$N$$ atoms are attached to hydrogen atom.
247.
In which of the following molecules are all the bonds not equal? A
$$Cl{F_3}$$
B
$$B{F_3}$$
C
$$Al{F_3}$$
D
$$N{F_3}$$
Answer :
$$Cl{F_3}$$
View Solution
Discuss Question
In $$Cl{F_3}$$ all bonds are not equal due to its trigonal-bipyramidal ($$s{p^3}d$$ hybridisation) geometry
$$B{F_3}$$ and $$Al{F_3}$$ show trigonal symmetric structure due to $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation.
$$N{F_3}$$ shows pyramidal geometry due to $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation.
248.
The weakest among the following types of bond is A
ionic
B
covalent
C
metallic
D
$$H$$-bond
Answer :
$$H$$-bond
View Solution
Discuss Question
$$H$$ -bond is weakest bond because its bond dissociation energy is very low as compared to other given bonds $$\left( {10\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}} \right).$$
249.
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than $$p{\text{ - }}$$ and $$m{\text{ - }}$$ Nitrophenols because : A
$$o{\text{ - }}$$Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of
$$m{\text{ - }}$$ and $$p{\text{ - }}$$isomers.
B
$$o{\text{ - }}$$Nitrophenol shows intramolecular $$H$$ - bonding
C
$$o{\text{ - }}$$Nitrophenol shows intermolecular $$H$$ - bonding
D
Melting point of $$o{\text{ - }}$$Nitrophenol is lower than those of $$m{\text{ - }}$$ and $$p{\text{ - }}$$isomers.
Answer :
$$o{\text{ - }}$$Nitrophenol shows intramolecular $$H$$ - bonding
View Solution
Discuss Question
Compounds involved in chelation become non-polar. Consequently such compounds are soluble in nonpolar solvents like ether, benzene etc. and are only sparingly soluble in water whereas meta and para isomers are more soluble in water & less soluble in non-polar solvents.
250.
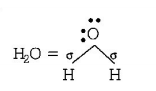
In which of the following molecules/ions $$B{F_3},NO_2^ - ,NH_2^ - \,{\text{and}}\,{H_2}O,$$ the central atom is $$s{p^2}$$ hybridised? A
$$NO_2^ - \,{\text{and}}\,NH_2^ - $$
B
$$NH_2^ - \,{\text{and}}\,{H_2}O$$
C
$$NO_2^ - \,{\text{and}}\,{H_2}O$$
D
$$B{F_3}\,{\text{and}}\,NO_2^ - $$
Answer :
$$B{F_3}\,{\text{and}}\,NO_2^ - $$
View Solution
Discuss Question
$$B{F_3}$$
$$ \Rightarrow 3\sigma $$ - bonds, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation
Planar structure
$$NO_2^ - $$
$$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+1$$ lone pair of
electrons, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation
$$NH_2^ - $$
$$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+2$$ lone pairs, i.e. $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation
$$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+2$$ lone pairs, i.e. $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation, Thus, in $$B{F_3}$$ and $$NO_2^ - ,$$ central atom is $$s{p^2}$$ hybridised, while $$N{H_2},N{H_3}$$ and $${H_2}O$$ are $$s{p^3}$$ hybridised.




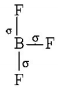 $$ \Rightarrow 3\sigma $$ - bonds, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation
$$ \Rightarrow 3\sigma $$ - bonds, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation 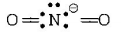 $$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+1$$ lone pair of
electrons, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation
$$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+1$$ lone pair of
electrons, i.e. $$s{p^2}$$ hybridisation 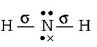 $$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+2$$ lone pairs, i.e. $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation
$$ \Rightarrow 2\sigma $$ - bonds $$+2$$ lone pairs, i.e. $$s{p^3}$$ hybridisation