31.
In a coil of resistance 100 $$\Omega ,$$ a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is

A
$$250\,Wb$$
B
$$275\,Wb$$
C
$$200\,Wb$$
D
$$225\,Wb$$
Answer :
$$250\,Wb$$
32.
One conducting $$U$$ tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field $$B$$ is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at
a constant speed $$v,$$ then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of $$B, l$$ and $$v$$ where $$l$$ is the width of each tube, will be
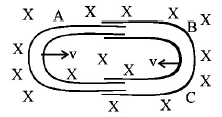
A
$$ - Blv$$
B
$$Blv$$
C
$$2Blv$$
D
zero
Answer :
$$2Blv$$
33. A varying current in a coil changes from $$10\,A$$ to zero in $$0.5\,s.$$ If the average emf induced in the coil is $$220\,V,$$ the self-inductance of the coil is
A
$$5\,H$$
B
$$6\,H$$
C
$$11\,H$$
D
$$12\,H$$
Answer :
$$11\,H$$
34. A coil having $$n$$ turns and resistance $$R\Omega $$ is connected with a galvanometer of resistance $$4R\Omega .$$ This combination is moved in time $$t$$ seconds from a magnetic field $${W_1}$$ weber to $${W_2}$$ weber. The induced current in the circuit is
A
$$ - \frac{{\left( {{W_2} - {W_1}} \right)}}{{Rnt}}$$
B
$$ - \frac{{n\left( {{W_2} - {W_1}} \right)}}{{5Rt}}$$
C
$$ - \frac{{\left( {{W_2} - {W_1}} \right)}}{{5Rnt}}$$
D
$$ - \frac{{n\left( {{W_2} - {W_1}} \right)}}{{Rt}}$$
Answer :
$$ - \frac{{n\left( {{W_2} - {W_1}} \right)}}{{5Rt}}$$
35. A simple electric motor has an armature resistance of $$1\,\Omega $$ and runs from a dc source of 12 volt. When running unloaded it draws a current of $$2\,amp.$$ When a certain load is connected, its speed. becomes one-half of its unloaded value. What is the new value of current drawn?
A
$$7\,A$$
B
$$3\,A$$
C
$$5\,A$$
D
$$4\,A$$
Answer :
$$7\,A$$
36.
In a coil of resistance $$100\,\Omega ,$$ a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is
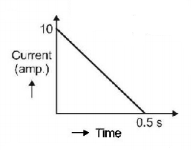
A
$$250\,Wb$$
B
$$275\,Wb$$
C
$$200\,Wb$$
D
$$225\,Wb$$
Answer :
$$250\,Wb$$
37.
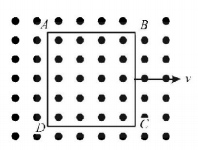
A metallic square loop $$ABCD$$ is moving in its own plane with velocity $$v$$ in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in the figure. An electric field is induced
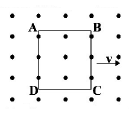
A
in $$AD,$$ but not in $$BC$$
B
in $$BC,$$ but not in $$AD$$
C
neither in $$AD$$ nor in $$BC$$
D
in both $$AD$$ and $$BC$$
Answer :
in both $$AD$$ and $$BC$$
38.
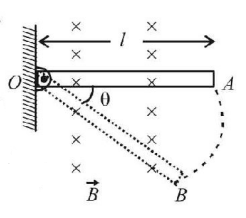
A conducting rod of length $$l$$ is hinged at point $$O.$$ It is free to rotate in vertical plane. There exists a uniform magnetic field $${\vec B}$$ in horizontal direction. The rod is released from position shown in the figure. When rod makes an angle $$\theta $$ from released position then potential difference between two ends of the rod is proportional to:
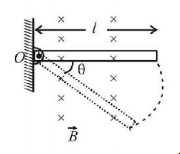
A
$${l^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
B
The lower end will be at a lower potential
C
$$\sin \theta $$
D
$${\left( {\sin \theta } \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
Answer :
$${\left( {\sin \theta } \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
39. A rectangular coil of 20 turns and area of cross-section $$25\,sq\,cm$$ has a resistance of $$100\,\Omega .$$ If a magnetic field which is perpendicular to the plane of coil changes at a rate of $$1000\,T/s,$$ the current in the coil is
A
$$1\,A$$
B
$$50\,A$$
C
$$0.5\,A$$
D
$$5\,A$$
Answer :
$$0.5\,A$$
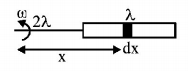
40.
A metallic rod of length $$'\ell '$$ is tied to a string of length $$2\ell $$ and made to rotate with angular speed $$w$$ on a horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If there is a vertical magnetic field $$'B'$$ in the region, the e.m.f. induced across the ends of the rod is
A
$$\frac{{2B\omega {\ell ^2}}}{2}$$
B
$$\frac{{3B\omega {\ell ^2}}}{2}$$
C
$$\frac{{4B\omega {\ell ^2}}}{2}$$
D
$$\frac{{5B\omega {\ell ^2}}}{2}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{5B\omega {\ell ^2}}}{2}$$