261. The hybridisation of carbons of $$C - C$$ single bond of $$HC \equiv C - CH = C{H_2}$$ is
A
$$s{p^3} - s{p^3}$$
B
$$sp - s{p^2}$$
C
$$s{p^3} - sp$$
D
$$s{p^2} - s{p^3}$$
Answer :
$$sp - s{p^2}$$
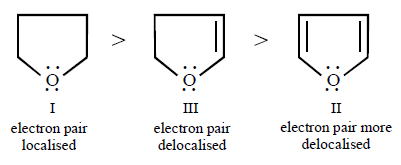
262.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water
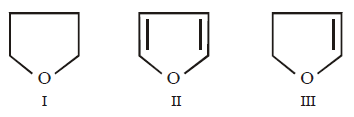
A
I > III > II
B
III > II > I
C
II > III > I
D
All are equally soluble
Answer :
I > III > II
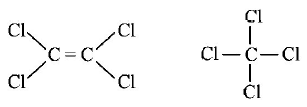
263. The $$Cl - C - Cl$$ angle in 1, 1, 2, 2 - tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about
A
$${120^ \circ }\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{109.5^ \circ }$$
B
$${90^ \circ }\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{109.5^ \circ }$$
C
$${109.5^ \circ }\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{90^ \circ }$$
D
$${109.5^ \circ }\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{120^ \circ }$$
Answer :
$${120^ \circ }\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,{109.5^ \circ }$$
264. IUPAC name of $${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_3}C - CH = C{H_2}$$ is
A
2, 2-dimethylbut-3-ene
B
2, 2-dimethylpent -4-ene
C
3, 3-dimethylbut -1-ene
D
hex-1-ene
Answer :
3, 3-dimethylbut -1-ene
265. The correct order of increasing basicity of the given conjugate bases $$\left( {R = C{H_3}} \right)$$ is
A
$$RCO\overline O < HC \equiv \overline C < \overline R < \overline N {H_2}$$
B
$$\overline R < HC \equiv \overline C < RCO\overline O < \overline N {H_2}$$
C
$$RCO\overline O < \overline N {H_2} < HC \equiv \overline C < \overline R $$
D
$$RCO\overline O < HC \equiv \overline C < \overline N {H_2} < \overline R $$
Answer :
$$RCO\overline O < HC \equiv \overline C < \overline N {H_2} < \overline R $$
266. Which one of the following acids would you expect to be the strongest?
A
$$I - C{H_2}COOH$$
B
$$Cl - C{H_2}COOH$$
C
$$Br - C{H_2}COOH$$
D
$$F - C{H_2}COOH$$
Answer :
$$F - C{H_2}COOH$$
267. The pair of electron in the given carbanion, $$C{H_3}C \equiv {C^ - },$$ is present in which orbitals?
A
$$s{p^3}$$
B
$$s{p^2}$$
C
$$sp$$
D
$$2p$$
Answer :
$$sp$$
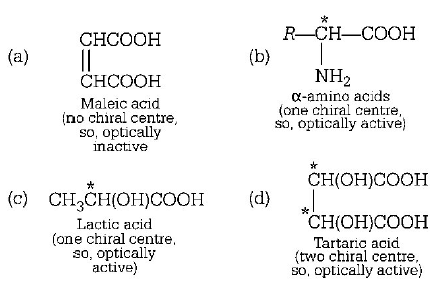
268. Which of the following acid does not exhibit optical isomerism?
A
Maleic acid
B
$$\alpha $$ - amino acid
C
Lactic acid
D
Tartaric acid
Answer :
Maleic acid
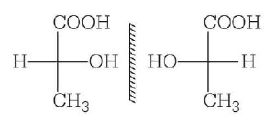
269. Two possible stereo-structures of $$C{H_3}CHOH \cdot COOH,$$ which are optically active, are called
A
diastereomers
B
atropisomers
C
enantiomers
D
mesomers
Answer :
enantiomers
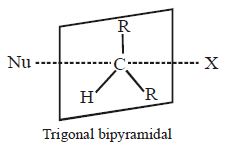
270.
The shape of transition state is –
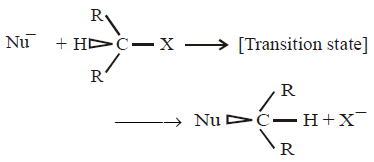
A
Triangular planar
B
Square pyramidal
C
Trigonal bipyramidal
D
Tetrahedral
Answer :
Trigonal bipyramidal