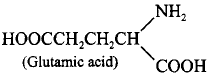191. The helical structure of protein is stabilised by
A
dipeptide bonds
B
hydrogen bonds
C
ether bonds
D
peptide bonds
Answer :
hydrogen bonds
192. Secondary structure of protein refers to
A
sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
B
bonds between alternate polypeptide chains
C
folding patterns of polypeptide chain
D
bonding between $$NH_3^ + $$ and $$CO{O^ - }$$ of two peptides
Answer :
folding patterns of polypeptide chain
193. In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by
A
van der Waals forces
B
electrostatic forces of attraction
C
hydrogen bonds
D
covalent bonds
Answer :
hydrogen bonds
194. Cellulose is a
A
hexapolysaccharide
B
pentapolysaccharide
C
tripolysaccharide
D
none of these
Answer :
none of these
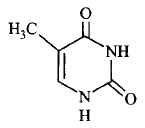
195. Thymine is
A
1-methyluracil
B
4-methyluracil
C
3-methyluracil
D
5-methyluracil
Answer :
5-methyluracil
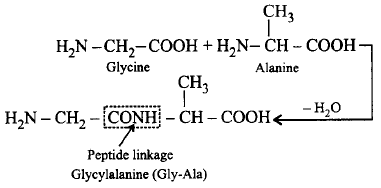
196. The peptide linkage formed between glycine \[\left( N{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH \right)\] and alanine \[(\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} \,| \\ \,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}} \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{N{{H}_{2}}CH-}}\,COOH)\] to give glycylalanine can be shown as
A
\[N{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-NH\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,COOH\]
B
\[N{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CONH\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,COOH\]
C
\[{{H}_{2}}NCOC{{H}_{2}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,CON{{H}_{2}}\]
D
\[HOOC-C{{H}_{2}}-NH-NH\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,COOH\]
Answer :
\[N{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CONH\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,COOH\]
197. Glucose reacts with Tollens' reagent to give a derivative of
A
monocarboxylic acid
B
dicarboxylic acid
C
ketone
D
keto acid
Answer :
monocarboxylic acid
198. Which of the following is an acidic amino acid?
A
Glycine
B
Valine
C
Leucine
D
Glutamic acid
Answer :
Glutamic acid
199.
The correct statement about the following disaccharide
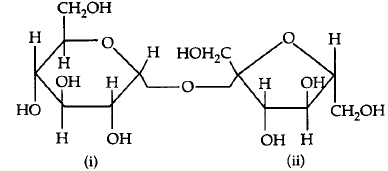
A
ring (i) is pyranose with $$\alpha {\text{ - }}$$glycosidic linkage
B
ring (i) is furanose with $$\alpha {\text{ - }}$$glycosidic linkage
C
ring (ii) is pyranose with $$\alpha {\text{ - }}$$glycosidic linkage
D
ring (ii) is pyranose with $$\beta {\text{ - }}$$glycosidic linkage
Answer :
ring (i) is pyranose with $$\alpha {\text{ - }}$$glycosidic linkage
200. Among the following vitamins the one whose deficiency causes rickets ( bone deficiency ) is
A
Vitamin $$A$$
B
Vitamin $$B$$
C
Vitamin $$D$$
D
Vitamin $$C$$
Answer :
Vitamin $$D$$