181. Which one of the following sets of monosaccharides forms sucrose?
A
$$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ galactopyranose and $$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ glucopyranose
B
$$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ glucopyranose and $$\beta {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ fructofuranose
C
$$\beta {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ glucopyranose and $$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ fructofuranose
D
$$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ glucopyranose and $$\beta {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ fructopyranose
Answer :
$$\alpha {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ glucopyranose and $$\beta {\text{ - }}D{\text{ - }}$$ fructofuranose
182. $$RNA$$ is different from $$DNA$$ because $$RNA$$ contains
A
ribose sugar and thymine
B
ribose sugar and uracil
C
deoxyribose sugar and thymine
D
deoxyribose sugar and uracil
Answer :
ribose sugar and uracil
183. Nucleotides in $$DNA$$ are linked by –
A
hydrogen bond
B
$$3',5'{\text{ - }}$$ phosphodiester bond
C
glycosidic bond
D
peptide bond
Answer :
$$3',5'{\text{ - }}$$ phosphodiester bond
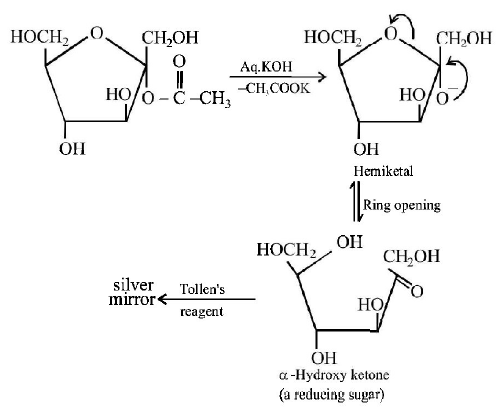
184. Which of the following compounds will behave as a reducing sugar in an aqueous $$KOH$$ solution?
A
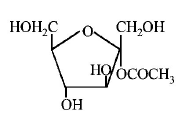

B


C
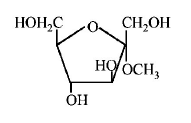

D
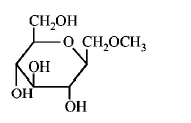

Answer :


185. Which of the following statements is not true?
A
Glucose and fructose both are monosaccharides.
B
The natural glucose and fructose are $$D$$ - forms.
C
The solution having equal molecules of $$D$$ - glucose and $$D$$ - fructose is termed as invert sugar.
D
Aldohexoses exist in $${2^6}$$ optical forms.
Answer :
Aldohexoses exist in $${2^6}$$ optical forms.
186. The letter $$'D'$$ in carbohydrates signifies
A
dextrorotatory
B
configuration
C
diamagnetic nature
D
mode of synthesis
Answer :
configuration
187.
Match List $$I$$ ( name of vitamin ) with List $$II$$ ( deficiency result/disease ) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists :
List I
List II
1.
Ascorbic acid
a.
Beri-beri
2.
Retinol
b.
Cracked lips
3.
Riboflavin
c.
Scurvy
4.
Thiamine
d.
Night blindness
A
1 - b, 2 - a, 3 - c, 4 - d
B
1 - a, 2 - b, 3 - c, 4 - d
C
1- d, 2 - c, 3 - b, 4 - a
D
1 - c, 2 - d, 3 - b, 4 - a
Answer :
1 - c, 2 - d, 3 - b, 4 - a
188. The two forms of $$D - $$ glucopyranose obtained from the solution of $$D - $$ glucose are called
A
Isomers
B
Anomers
C
Epimers
D
Enantiomers
Answer :
Anomers
189. If one strand of $$DNA$$ has the sequence $$ATGCTTGA,$$ the sequence in the complimentary strand would be
A
$$TACGAACT$$
B
$$TCCGAACT$$
C
$$TACGTACT$$
D
$$TACGTAGT$$
Answer :
$$TACGAACT$$
190. Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
A
Glucose forms pentaacetate.
B
Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
C
Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
D
Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid.
Answer :
Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.