431. Sulphuric acid reacts with $$PC{l_5}$$ to give
A
thionyl chloride
B
sulphur monochloride
C
sulphuryl chloride
D
sulphur tetrachloride
Answer :
sulphuryl chloride
432. By which of the following $$S{O_2}$$ is formed ?
A
Reaction of $$dil.{H_2}S{O_4}$$ with $${O_2}$$
B
Hydrolysis of $$dil.{H_2}S{O_4}$$
C
Reaction of $$conc.\,{H_2}S{O_4}$$ with $$Cu$$
D
None of these
Answer :
Reaction of $$conc.\,{H_2}S{O_4}$$ with $$Cu$$
433. When white phosphorus is heated at $$473\,K$$ under high pressure, what will happen?
A
$$\alpha $$ - Black phosphorus is formed.
B
$$\beta $$ - Black phosphorus is formed.
C
Red phosphorus is formed.
D
No change would be observed.
Answer :
$$\beta $$ - Black phosphorus is formed.
434. On reaction with $$C{l_2},$$ phosphorus forms two types of halides $$'A'$$ and $$'B'.$$ Halide $$'A'$$ is yellowish-white powder but halide $$'B'$$ is colourless oily liquid. What would be the hydrolysis products of $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$ respectively?
A
$${H_3}P{O_4},{H_3}P{O_3}$$
B
$$HOP{O_3},{H_2}P{O_2}$$
C
$${H_3}P{O_3},{H_3}P{O_4}$$
D
$$HP{O_3},{H_3}P{O_3}$$
Answer :
$${H_3}P{O_4},{H_3}P{O_3}$$
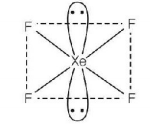
435. The correct geometry and hybridisation for $$Xe{F_4}$$ are
A
octahedral, $$s{p^3}{d^2}$$
B
trigonal bipyramidal, $$s{p^3}d$$
C
planar triangle, $$s{p^3}{d^3}$$
D
square planar, $$s{p^3}{d^2}$$
Answer :
octahedral, $$s{p^3}{d^2}$$
436. Name of the structure of silicates in which three oxygen atoms of $${\left[ {Si{O_4}} \right]^{4 - }}$$ are shared.
A
Pyrosilicate
B
Sheet silicate
C
Linear chain silicate
D
Three dimensional silicate
Answer :
Sheet silicate
437. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
A
Acidic oxides - $${P_2}{O_5},N{O_2},C{l_2}{O_7}$$
B
Basic oxides - $$N{a_2}O,CaO,MgO$$
C
Neutral oxides - $$C{O_2},CO,BeO$$
D
Amphoteric oxides - $$ZnO,SnO,A{l_2}{O_3}$$
Answer :
Neutral oxides - $$C{O_2},CO,BeO$$
438. Which of the following statements about anhydrous aluminium chloride is correct?
A
it exists as $$AIC{l_3}$$ molecules
B
it is not easily hydrolysed
C
it sublimes at $${100^ \circ }$$ under vacuum
D
it is a strong Lewis base
Answer :
it sublimes at $${100^ \circ }$$ under vacuum
439. Which is the hardest compound of boron?
A
$${B_2}{O_3}$$
B
$${H_3}B{O_3}$$
C
$${B_4}C$$
D
$${B_2}{H_6}$$
Answer :
$${B_4}C$$
440. The order of the oxidation state of the phosphorus atom in $${H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_4},{H_3}P{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{{\text{H}}_4}{P_2}{O_6}\,\,{\text{is}}$$
A
$${H_3}P{O_3} > {H_3}P{O_2} > {H_3}P{O_4} > {H_4}{P_2}{O_6}$$
B
$${H_3}P{O_4} > {H_3}P{O_2} > {H_3}P{O_3} > {H_4}{P_2}{O_6}$$
C
$${H_3}P{O_4} > {H_4}{P_2}{O_6} > {H_3}P{O_3} > \,{H_3}P{O_2}$$
D
$${H_3}P{O_2} > {H_3}P{O_3} > {H_4}{P_2}{O_6} > {H_3}P{O_4}$$
Answer :
$${H_3}P{O_4} > {H_4}{P_2}{O_6} > {H_3}P{O_3} > \,{H_3}P{O_2}$$