Releted MCQ Question on
Organic Chemistry >> Biomolecules
Releted Question 1
The pair of compounds in which both the compounds give positive test with Tollen’s reagent is
A.
Glucose and Sucrose
B.
Fructose and Sucrose
C.
Acetophenone and Hexanal
D.
Glucose and Fructose
Releted Question 2
The two forms of $$D - $$ glucopyranose obtained from the solution of $$D - $$ glucose are called
A.
Isomers
B.
Anomers
C.
Epimers
D.
Enantiomers
Releted Question 3
Cellulose upon acetylation with excess acetic anhydride/ $${H_2}S{O_4}$$ (catalytic) gives cellulose triacetate whose structure is
A.
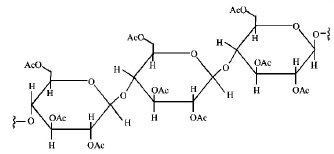

B.
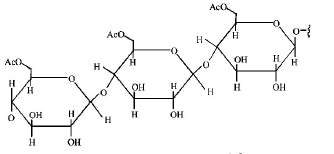

C.
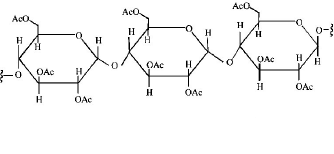

D.
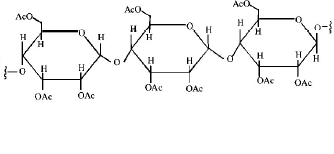

Releted Question 4
The following carbohydrate is
The following carbohydrate is

A.
a ketohexose
B.
an aldohexose
C.
an $$\alpha $$ - furanose
D.
an $$\alpha $$ - pyranose