Question
When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory in the absence of enzyme then rate of reaction obtained is $${10^{ - 6}}$$ times, then activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is
A.
$$\frac{6}{{RT}}$$
B.
different from $${E_a}$$ obtained in laboratory
C.
$$P$$ is required
D.
can't say anything
Answer :
different from $${E_a}$$ obtained in laboratory
Solution :
The presence of enzyme (catalyst) increases the speed of reaction by lowering the energy barrier, i.e., a new path is followed with lower activation energy.
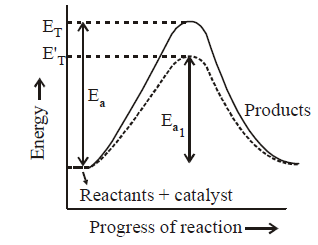
Here $${E_T}$$ is the threshold energy. $${E_a}$$ and $${E_{a1}}$$ is energy of activation of reaction in absence and presence of catalyst respectively.
The presence of enzyme (catalyst) increases the speed of reaction by lowering the energy barrier, i.e., a new path is followed with lower activation energy.

Here $${E_T}$$ is the threshold energy. $${E_a}$$ and $${E_{a1}}$$ is energy of activation of reaction in absence and presence of catalyst respectively.