Question
The temperature dependence of rate constant $$\left( k \right)$$ of a chemical reaction is written in terms of Arrhenius equation, $$k = A{e^{ - \,\frac{{{E^*}}}{{RT}}}}.$$ Activation energy $$\left( {{E^*}} \right)$$ of the reaction can be calculated by plotting
A.
$${\text{log}}\,k\,\,{\text{vs}}\,\,\frac{1}{T}$$
B.
$${\text{log}}\,k\,\,{\text{vs}}\,\,\frac{1}{{{\text{log}}\,T}}$$
C.
$$k\,\,{\text{vs}}\,\,T$$
D.
$$k\,\,{\text{vs}}\,\,\frac{1}{{\log \,T}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{log}}\,k\,\,{\text{vs}}\,\,\frac{1}{T}$$
Solution :
$${\text{Arrhenius equation}}\,\,k = A{e^{ - \,\frac{{{E^*}}}{{RT}}}}$$
$$\ln \,k = \ln \,A - \frac{{{E^*}}}{{RT}}$$ ( $${{E^*} = }$$ energy of activation )
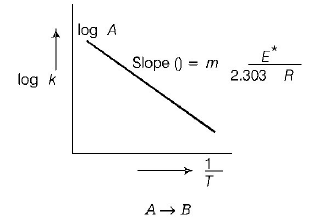
$${\text{or}}\,\,{\text{log}}\,k = {\text{log}}\,A = \frac{{{E^*}}}{{2.303\,RT}}$$
Compare this equation with the straight line equation,
$${\text{i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{.}}\,\,y = mx + c$$
where $$'m’$$ is slope and $$'c’$$ is intercept
Hence, $${E^*}$$ can be calculated with the help of following slope
$${\text{Arrhenius equation}}\,\,k = A{e^{ - \,\frac{{{E^*}}}{{RT}}}}$$
$$\ln \,k = \ln \,A - \frac{{{E^*}}}{{RT}}$$ ( $${{E^*} = }$$ energy of activation )
$${\text{or}}\,\,{\text{log}}\,k = {\text{log}}\,A = \frac{{{E^*}}}{{2.303\,RT}}$$
Compare this equation with the straight line equation,
$${\text{i}}{\text{.e}}{\text{.}}\,\,y = mx + c$$
where $$'m’$$ is slope and $$'c’$$ is intercept
Hence, $${E^*}$$ can be calculated with the help of following slope
