Question
Reaction of $$HBr$$ with propene in the presence of peroxide gives
A.
$$iso$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide$$
B.
3 - $$bromo$$ $$propane$$
C.
$$allyl$$ $$bromide$$
D.
$$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide$$
Answer :
$$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide$$
Solution :
Reaction of $$HBr$$ with propene in the presence of peroxide gives $$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide.$$ This addition teaction is an example of anti-Markownikoff's addition reaction.
( i.e. it is completed in form of free radical addition )
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HBr\xrightarrow{\text{Peroxide}}\] \[\underset{n\text{-propyl bromide}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}BR}}\,\]
Mechanism of this reaction is represented as follows :
Step (i) Formation of free radical of peroxide by means of decomposition.
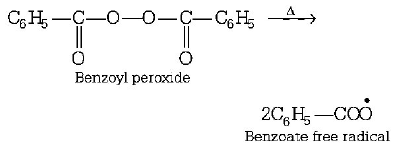
Step (ii) Benzoate free radical forms bromine free radical with $$HBr.$$
$${C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O + H - Br \to $$ $${C_6}{H_5}COOH + B\dot r$$
Step (iii) Bromine free radical attacks on $$C=C$$ of propene to form intermediate free radical.

Hence, $$C{H_3} - \dot CH - C{H_2}Br$$ is the major product of this step.
Step (iv) More stable free radical accept hydrogen free radical from benzoic acid and give final product of reaction. i.e. $$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide.$$
$$C{H_3} - \dot CH - C{H_2}Br + {C_6}{H_5}COOH$$ $$ \to \mathop {C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2}Br}\limits_{n{\text{ - propyl bromide}}} + {C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O$$
Step V Benzoate free radicals are changed into benzoyl peroxide for the termination of free radical chain.
$${C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O + {C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O$$ $$ \to {\left( {{C_6}{H_5}COO} \right)_2}$$
Reaction of $$HBr$$ with propene in the presence of peroxide gives $$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide.$$ This addition teaction is an example of anti-Markownikoff's addition reaction.
( i.e. it is completed in form of free radical addition )
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HBr\xrightarrow{\text{Peroxide}}\] \[\underset{n\text{-propyl bromide}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}BR}}\,\]
Mechanism of this reaction is represented as follows :
Step (i) Formation of free radical of peroxide by means of decomposition.

Step (ii) Benzoate free radical forms bromine free radical with $$HBr.$$
$${C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O + H - Br \to $$ $${C_6}{H_5}COOH + B\dot r$$
Step (iii) Bromine free radical attacks on $$C=C$$ of propene to form intermediate free radical.

Hence, $$C{H_3} - \dot CH - C{H_2}Br$$ is the major product of this step.
Step (iv) More stable free radical accept hydrogen free radical from benzoic acid and give final product of reaction. i.e. $$n$$ - $$propyl$$ $$bromide.$$
$$C{H_3} - \dot CH - C{H_2}Br + {C_6}{H_5}COOH$$ $$ \to \mathop {C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2}Br}\limits_{n{\text{ - propyl bromide}}} + {C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O$$
Step V Benzoate free radicals are changed into benzoyl peroxide for the termination of free radical chain.
$${C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O + {C_6}{H_5}CO\dot O$$ $$ \to {\left( {{C_6}{H_5}COO} \right)_2}$$