41. Radius of moon is $$\frac{1}{4}$$ times that of earth and mass is $$\frac{1}{81}$$ times that of earth. The point at which gravitational field due to earth becomes equal and opposite to that of moon, is (Distance between centres of earth and moon is $$60R,$$ where $$R$$ is radius of earth)
A
$$5.75\,R$$ from centre of moon
B
$$16\,R$$ from surface of moon
C
$$53\,R$$ from centre of earth
D
$$54\,R$$ from centre of earth
Answer :
$$54\,R$$ from centre of earth
42. Two satellites of the earth, $${S_1}$$ and $${S_2}$$ are moving in the same orbit. The mass of $${S_1}$$ is four times the mass of $${S_2}.$$ Which one of the following statements is true?
A
The time period of $${S_1}$$ is four times that of $${S_2}$$
B
The potential energies of the earth and satellite in the two cases are equal
C
$${S_1}$$ and $${S_2}$$ are moving with the same speed
D
The kinetic energies of the two satellites are equal
Answer :
$${S_1}$$ and $${S_2}$$ are moving with the same speed
43. A space vehicle approaching a planet has a speed $$v,$$ when it is very far from the planet. At that moment tangent of its trajectory would miss the centre of the planet by distance $$R.$$ If the planet has mass $$M$$ and radius $$r,$$ what is the smallest value of $$R$$ in order that the resulting orbit of the space vehicle will just miss the surface of the planet?
A
$$\frac{r}{v}{\left[ {{v^2} + \frac{{2GM}}{r}} \right]^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
B
$$vr\left[ {1 + \frac{{2GM}}{r}} \right]$$
C
$$\frac{r}{v}\left[ {{v^2} + \frac{{2GM}}{r}} \right]$$
D
$$\frac{{2GMv}}{r}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{r}{v}{\left[ {{v^2} + \frac{{2GM}}{r}} \right]^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
44. An artificial satellite is first taken to a height equal to half the radius of earth. Assume that it is at rest on the earth’s surface initially and that it is at rest at this height. Let $${{E_1}}$$ be the energyrequired. It is then given the appropriate orbital speed such that it goes in a circular orbit at that height. Let $${{E_1}}$$ be the energy required. The ratio $$\frac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}}$$ is
A
$$4:1$$
B
$$3:1$$
C
$$1:1$$
D
$$1:2$$
Answer :
$$1:1$$
45. Energy required to move a body of mass $$m$$ from an orbit of radius $$2R$$ to $$3R$$ is-
A
$$\frac{{GMm}}{{12{R^2}}}$$
B
$$\frac{{GMm}}{{3{R^2}}}$$
C
$$\frac{{GMm}}{{8R}}$$
D
$$\frac{{GMm}}{{6R}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{GMm}}{{6R}}$$
46. What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass $$m$$ from the surface of a planet of mass $$M$$ and radius $$R$$ in a circular orbit at an altitude of $$2R?$$
A
$$\frac{{5GmM}}{{6R}}$$
B
$$\frac{{2GmM}}{{3R}}$$
C
$$\frac{{GmM}}{{2R}}$$
D
$$\frac{{GmM}}{{3R}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{5GmM}}{{6R}}$$
47.
Three particles $$P,Q$$ and $$R$$ are placed as per given figure. Masses of $$P,Q$$ and $$R$$ are $$\sqrt 3 m,\sqrt 3 m$$ and $$m$$ respectively. The gravitational force on a fourth particle $$S$$ of mass $$m$$ is equal to
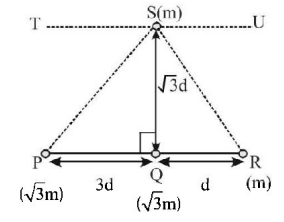
A
$$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$ST$$ direction only
B
$$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$SQ$$ direction and $$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$SU$$ direction
C
$$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$SQ$$ direction only
D
$$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$SQ$$ direction and $$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$ST$$ direction
Answer :
$$\frac{{\sqrt 3 G{M^2}}}{{2{d^2}}}$$ in $$SQ$$ direction only
48. The ratio of escape velocity at earth $$\left( {{v_e}} \right)$$ to the escape velocity at a planet $$\left( {{v_p}} \right)$$ whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is
A
$$1:2\sqrt 2 $$
B
$$1:4$$
C
$$1:\sqrt 2 $$
D
$$1:2$$
Answer :
$$1:2\sqrt 2 $$
49. A ball is dropped from a satellite revolving around the earth at a height of $$120\,km.$$ The ball will
A
continue to move with same speed along a straight line tangentially to the satellite at that time
B
continue to move with the same speed along the original orbit of satellite
C
fall down to the earth gradually
D
go far away in space
Answer :
continue to move with the same speed along the original orbit of satellite
50. A seconds pendulum is mounted in a rocket. Its period of oscillation decreases when the rocket
A
comes down with uniform acceleration
B
moves round the earth in a geostationary orbit
C
moves up with a uniform velocity
D
moves up with uniform acceleration
Answer :
moves up with uniform acceleration