21. A system consists of two stars of equal masses that revolve in a circular orbit about a centre of mass midway between them. Orbital speed of each star is $$v$$ and period is $$T.$$ Find the mass $$M$$ of each star ($$G$$ is gravitational constant)
A
$$\frac{{2G{v^3}}}{{\pi T}}$$
B
$$\frac{{{v^3}T}}{{\pi G}}$$
C
$$\frac{{{v^3}T}}{{2\pi G}}$$
D
$$\frac{{2T{v^3}}}{{\pi G}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{2T{v^3}}}{{\pi G}}$$
22. The distance of Neptune and Saturn from the sun is nearly $${10^{13}}$$ and $${10^{12}}$$ meter respectively. Assuming that they move in circular orbits, their periodic times will be in the ratio
A
$$10$$
B
$$100$$
C
$$10\sqrt {10} $$
D
$$1000$$
Answer :
$$10\sqrt {10} $$
23. A uniform spherical shell gradually shrinks maintaining its shape. The gravitational potential at the centre
A
increases
B
decreases
C
remains constant
D
cannot say
Answer :
increases
24. A rubber ball is dropped from a height of $$5\,m$$ on a planet where the acceleration due to gravity is not known. On bouncing it rises to $$1.8\,m.$$ The ball loses its velocity on bouncing by a factor of
A
$$\frac{{16}}{{25}}$$
B
$$\frac{2}{5}$$
C
$$\frac{3}{5}$$
D
$$\frac{9}{{25}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{2}{5}$$
25.
The depth $$d$$ at which the value of acceleration due to gravity becomes $$\frac{1}{n}$$ times the value at the surface of the earth, is
[$$R$$ = radius of the earth]
A
$$\frac{R}{n}$$
B
$$R\left( {\frac{{n - 1}}{n}} \right)$$
C
$$\frac{R}{{{n^2}}}$$
D
$$R\left( {\frac{n}{{n + 1}}} \right)$$
Answer :
$$R\left( {\frac{{n - 1}}{n}} \right)$$
26. A spherical planet has a mass $${M_p}$$ and diameter $${D_p}.$$ A particle of mass $$m$$ falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity, equal to
A
$$\frac{{4G{M_p}}}{{D_p^2}}$$
B
$$\frac{{G{M_p}m}}{{D_p^2}}$$
C
$$\frac{{G{M_p}}}{{D_p^2}}$$
D
$$\frac{{4G{M_p}m}}{{D_p^2}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{4G{M_p}}}{{D_p^2}}$$
27. The escape velocity of a sphere of mass $$m$$ is given by ($$G =$$ universal gravitational constant, $${M_e} =$$ mass of the earth and $${R_e} =$$ radius of the earth)
A
$$\sqrt {\frac{{G{M_e}}}{{{R_e}}}} $$
B
$$\sqrt {\frac{{2G{M_e}}}{{{R_e}}}} $$
C
$$\sqrt {\frac{{2GM}}{{{R_e}}}} $$
D
$$\frac{{G{M_e}}}{{R_e^2}}$$
Answer :
$$\sqrt {\frac{{2G{M_e}}}{{{R_e}}}} $$
28. At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and the value of $$g$$ are $$ - 5.4 \times {10^7}J\,k{g^{ - 2}}$$ and $$6.0\,m{s^{ - 2}}$$ respectively? Take, the radius of earth as $$6400\,km.$$
A
$$1600\,km$$
B
$$1400\,km$$
C
$$2000\,km$$
D
$$2600\,km$$
Answer :
$$2600\,km$$
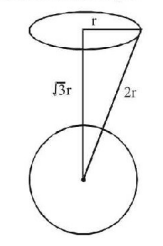
29.
A uniform ring of mass $$m$$ and radius $$r$$ is placed directly above a uniform sphere of mass $$M$$ and of equal radius. The centre of the ring is directly above the centre of the sphere at a distance $$r\sqrt 3 $$ as shown in the figure. The gravitational field due to the ring at a distance $$\sqrt 3 r$$ is
A
$$\frac{{Gm}}{{8{r^2}}}$$
B
$$\frac{{Gm}}{{4{r^2}}}$$
C
$$\sqrt 3 \frac{{Gm}}{{8{r^2}}}$$
D
$$\frac{{Gm}}{{8{r^2}\sqrt 3 }}$$
Answer :
$$\sqrt 3 \frac{{Gm}}{{8{r^2}}}$$
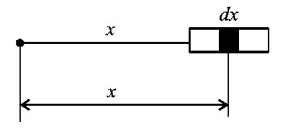
30. A straight rod of length $$L$$ extends from $$x = a$$ to $$x = L + a.$$ Find the gravitational force it exerts on a point mass $$m$$ at $$x = 0$$ if the linear density of rod $$\mu = A + B{x^2}.$$
A
$$Gm\left[ {\frac{A}{a} + BL} \right]$$
B
$$Gm\left[ {A\left( {\frac{1}{a} - \frac{1}{{a + L}}} \right) + BL} \right]$$
C
$$Gm\left[ {BL + \frac{A}{{a + L}}} \right]$$
D
$$Gm\left[ {BL - \frac{A}{a}} \right]$$
Answer :
$$Gm\left[ {A\left( {\frac{1}{a} - \frac{1}{{a + L}}} \right) + BL} \right]$$