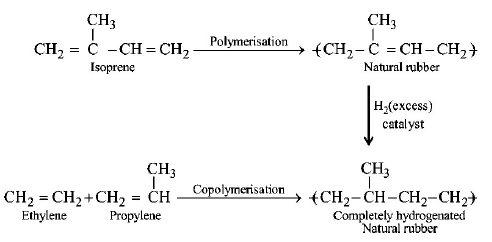
Question
On complete hydrogenation, natural rubber produces
A.
ethylene-propylene copolymer
B.
vulcanised rubber
C.
polypropylene
D.
polybutylene
Answer :
ethylene-propylene copolymer
Solution :