Question
Consider the reversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in a closed system at two different temperatures $${T_1}$$ and $${T_2}$$ $$\left( {{T_1} < {T_2}} \right).$$ The correct graphical depiction of the dependence of work done $$(w)$$ on the final volume $$(V)$$ is :
A.
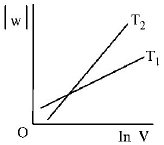

B.
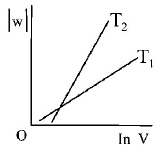

C.
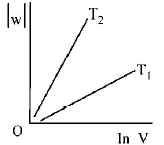

D.
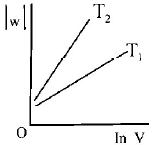

Answer :


Solution :
For reversible isothermal expansion,
$$\eqalign{ & w = - nRT\ln \frac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \cr & \therefore \,\left| w \right| = nRT\ln \frac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \cr & \left| w \right| = nRT\left( {\ln \,{V_2} - \ln {V_1}} \right) \cr & \left| w \right| = nRT\ln \,{V_2} - nRT{V_1} \cr & y = mx + c \cr} $$
So, slope of curve 2 is more than curve 1 and intercept of curve 2 is more negative than curve 1.
For reversible isothermal expansion,
$$\eqalign{ & w = - nRT\ln \frac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \cr & \therefore \,\left| w \right| = nRT\ln \frac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} \cr & \left| w \right| = nRT\left( {\ln \,{V_2} - \ln {V_1}} \right) \cr & \left| w \right| = nRT\ln \,{V_2} - nRT{V_1} \cr & y = mx + c \cr} $$
So, slope of curve 2 is more than curve 1 and intercept of curve 2 is more negative than curve 1.