271. A first order reaction is $$50\% $$ completed in $$1.26 \times {10^{14}}s.$$ How much time would it take for $$100\% $$ completion?
A
$$1.26 \times {10^{15}}s$$
B
$$2.52 \times {10^{14}}s$$
C
$$2.52 \times {10^{28}}s$$
D
$${\text{Infinite}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{Infinite}}$$
272. The rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes from $$300 K$$ to $$310 K.$$ Activation energy of such a reaction will be : $$\left( {R = 8.314\,J{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}\,{\text{and}}\,\log 2 = 0.301} \right)$$
A
$$53.6\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$48.6\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$58.5\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$60.5\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$53.6\,kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
273.
For a reaction, $${A_2} + {B_2} \rightleftharpoons 2AB$$ the figure shows the path of the reaction in absence and presence of a catalyst. What will be the energy of activation for forward $$\left( {{E_f}} \right)$$ and backward $$\left( {{E_b}} \right)$$ reaction in presence of a catalyst and $$\Delta H$$ for the reaction? The dotted curve is the path of reaction in presence of a catalyst.
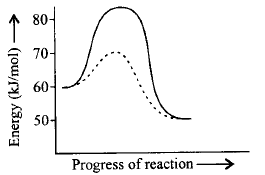
A
$${E_f} = 60\,kJ/mol,{E_b} = 70\,kJ/mol,$$ $$\Delta H = 20\,kJ/mol$$
B
$${E_f} = 20\,kJ/mol,{E_b} = 20\,kJ/mol,$$ $$\Delta H = 50\,kJ/mol$$
C
$${E_f} = 70\,kJ/mol,{E_b} = 20\,kJ/mol,$$ $$\Delta H = 10\,kJ/mol$$
D
$${E_f} = 10\,kJ/mol,{E_b} = 20\,kJ/mol,$$ $$\Delta H = - 10\,kJ/mol$$
Answer :
$${E_f} = 10\,kJ/mol,{E_b} = 20\,kJ/mol,$$ $$\Delta H = - 10\,kJ/mol$$
274. A radioactive isotope having a half - life period of 3 days was received after 12 days. If $$3g$$ of the isotope is left in the container, what would be the initial mass of the isotope?
A
12 $$g$$
B
36 $$g$$
C
48 $$g$$
D
24 $$g$$
Answer :
48 $$g$$
275. For the reaction, $$2{N_2}{O_5} \to 4N{O_2} + {O_2},$$ the rate equation can be expressed in two ways $$ - \frac{{d\left[ {{N_2}{O_5}} \right]}}{{dt}} = k\left[ {{N_2}{O_5}} \right]$$ and $$ + \frac{{d\left[ {N{O_2}} \right]}}{{dt}} = k'\left[ {{N_2}{O_5}} \right]$$ $$k$$ and $$k'$$ are related as :
A
$$k = k'$$
B
$$2k = k'$$
C
$$k = 2k'$$
D
$$k = 4k'$$
Answer :
$$2k = k'$$
276. The half-life period of a radioactive element is 140 days. After 560 days, one gram of the element will reduced to :
A
$$\frac{1}{2}g$$
B
$$\frac{1}{4}g$$
C
$$\frac{1}{8}g$$
D
$$\frac{1}{{16}}g$$
Answer :
$$\frac{1}{{16}}g$$
277. The rate constant of a zero order reaction is $$2.0 \times {10^{ - 2}}mol\,{L^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 1}}.$$ If the concentration of the reactant after 25 seconds is $$0.5\,M.$$ What is the initial concentration?
A
0.5$$\,M$$
B
1.25$$\,M$$
C
12.5$$\,M$$
D
1.0$$\,M$$
Answer :
1.0$$\,M$$
278. A first order reaction is half-completed in 45 minutes. How long does it need for $$99.9\% $$ of the reaction to be completed ?
A
$$20\,{\text{hours}}$$
B
$$10\,{\text{hours}}$$
C
$$7\frac{1}{2}\,{\text{hours}}$$
D
$$5\,{\text{hours}}$$
Answer :
$$7\frac{1}{2}\,{\text{hours}}$$
279.
$$\eqalign{
& A{g^ + } + N{H_3} \rightleftharpoons {\left[ {Ag\left( {N{H_3}} \right)} \right]^ + }\,;\,{k_1} = 6.8 \times {10^{ - 3}} \cr
& {\left[ {Ag\left( {N{H_3}} \right)} \right]^ + } + N{H_3} \rightleftharpoons {\left[ {Ag{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + };{k_2} = 1.6 \times {10^{ - 3}} \cr} $$
then the formation constant of $${\left[ {Ag{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_2}} \right]^ + }\,is$$
A
$$6.8 \times {10^{ - 6}}$$
B
$$1.08 \times {10^{ - 5}}$$
C
$$1.08 \times {10^{ - 6}}$$
D
$$6.8 \times {10^{ - 5}}$$
Answer :
$$1.08 \times {10^{ - 5}}$$
280.
The rate equation for a reaction,
$${N_2}O \to {N_2} + \frac{1}{2}{O_2}$$
is Rate $$ = k{\left[ {{N_2}O} \right]^0} = k.$$ If the initial concentration of the reactant is $$a\,mol\,Li{t^{ - 1}},$$ the half-life period of the reaction is
A
$${t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = \frac{a}{{2k}}$$
B
$$ - {t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = ka$$
C
$${t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = \frac{a}{k}$$
D
$${t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = \frac{k}{a}$$
Answer :
$${t_{\frac{1}{2}}} = \frac{a}{{2k}}$$