182. $$\beta - $$ particle is emitted in radioactivity by
A
conversion of proton to neutron
B
from outermost orbit
C
conversion of neutron to proton
D
$$\beta - $$ particle is not emitted.
Answer :
conversion of neutron to proton
183. The increase in concentration of the reactants lead to change in
A
$$\Delta H$$
B
collision frequency
C
activation energy
D
equilibrium constant
Answer :
collision frequency
184. For the reaction system : $$2NO\left( g \right) + {O_2}\left( g \right) \to 2N{O_2}\left( g \right)$$ volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order with respect to $${O_2}$$ and second order with respect to $$NO,$$ the rate of reaction will
A
diminish to one-eighth of its initial value
B
increase to eight times of its initial value
C
increase to four times of its initial value
D
diminish to one-fourth of its initial value
Answer :
increase to eight times of its initial value
185.
A homogeneous catalytic reaction takes place through the three alternative plots $$A,B$$ and $$C$$ shown in the given figure. Which one of the following indicates the relative ease with which the reaction can take place?
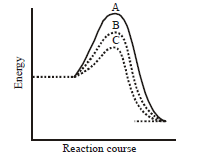
A
$$A > B > C$$
B
$$C > B > A$$
C
$$A > C > B$$
D
$$A = B = C$$
Answer :
$$C > B > A$$
186.
Rate law for the reaction, $$A + 2B \to C$$ is found to be
$${\text{Rate}} = k\left[ A \right]\left[ B \right]$$
Concentration of reactant $$'B'$$ is doubled, keeping the concentration of $$'A'$$ constant, the value of rate constant will be _________.
A
the same
B
doubled
C
quadrupled
D
halved
Answer :
the same
187. The radionucleide $$_{90}^{234}Th$$ undergoes two successive $$\beta - $$ decays followed by one $$\alpha - $$ decay. The atomic number and the mass number respectively of the resulting radionucleide are
A
94 and 230
B
90 and 230
C
92 and 230
D
92 and 234
Answer :
90 and 230
188. If uranium (mass number 238 and atomic number 92) emits an $$\alpha $$ -particle, the product has mass no. and atomic no.
A
236 and 92
B
234 and 90
C
238 and 90
D
236 and 90
Answer :
234 and 90
189. The half-life of a radioactive isotope is three hours. If the initial mass of the isotope were $$256 g,$$ the mass of it remaining undecayed after 18 hours would be
A
$$8.0 g$$
B
$$12.0 g$$
C
$$16.0 g$$
D
$$4.0 g$$
Answer :
$$4.0 g$$
190. Which of the following statements is correct?
A
The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decreases.
B
The rate of a reaction is same at any time during the reaction.
C
The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature change.
D
The rate of a reaction decreases with increase in concentration of reactant$$(s).$$
Answer :
The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decreases.