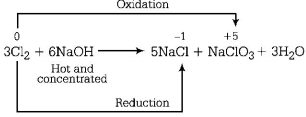
521. When $$C{l_2}$$ gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
A
zero to + 1 and zero to - 5
B
zero to - 1 and zero to + 5
C
zero to - 1 and zero to + 3
D
zero to + 1 and zero to - 3
Answer :
zero to - 1 and zero to + 5
522. Anhydrous $$AlC{l_3}$$ is prepared by
A
reaction of $$HCl$$ and $$Al$$ metal
B
reaction of dry $$HCl$$ gas and heated $$Al$$ metal
C
passing conc. $$HN{O_3}$$ gas over heated $$Al$$ metal
D
reaction of $$A{l_2}{O_3}$$ with $$dil.\,HCl$$
Answer :
reaction of dry $$HCl$$ gas and heated $$Al$$ metal
523. Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
A
$$CO_3^{2 - },NO_3^ - $$
B
$$ClO_3^ - ,CO_3^{2 - }$$
C
$$SO_3^{2 - },NO_3^ - $$
D
$$ClO_3^ - ,SO_3^{2 - }$$
Answer :
$$CO_3^{2 - },NO_3^ - $$
524. Identify the incorrect statement among the following.
A
$$B{r_2}$$ reacts with hot and strong $$NaOH$$ solution to give $$NaBr\,{\text{and}}\,{H_2}O$$.
B
Ozone reacts with $$S{O_2}$$ to give $$S{O_3}$$ .
C
Silicon reacts with $$NaO{H_{\left( {aq} \right)}}$$ in the presence of air to give $$N{a_2}Si{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{H_2}O$$.
D
$$C{l_2}$$ reacts with excess of $$N{H_3}$$ to give $${N_2}$$ and $$HCl$$ .
Answer :
$$C{l_2}$$ reacts with excess of $$N{H_3}$$ to give $${N_2}$$ and $$HCl$$ .
525. White $$P$$ reacts with caustic soda. The products are $$P{H_3}$$ and $$Na{H_2}P{O_2}.$$ This reaction is an example of
A
Oxidation
B
Reduction
C
oxidation and reduction
D
Neutralisation
Answer :
oxidation and reduction
526. Group 16 elements have lower value of first ionisation enthalpy as compared to group 15 elements because
A
half filled $$p$$ - orbitals in group 15 elements are more stable
B
group 16 elements have smaller size than group 15 elements
C
group 16 elements contain double bond while group 15 elements have triple bond
D
group 16 elements have more number of electrons in $$p$$ - orbitals.
Answer :
half filled $$p$$ - orbitals in group 15 elements are more stable
527. In case of nitrogen, $$NC{l_3}$$ is possible but not $$NC{l_5}$$ while in case of phosphorous, $$PC{l_3}$$ as well as $$PC{l_5}$$ are possible. It is due to
A
availability of vacant $$d$$ orbitals in $$P$$ but not in $$N$$
B
lower electronegativity of $$P\,{\text{than}}\,N$$
C
lower tendency of $$H$$-bond formation in $$P\,{\text{than}}\,N$$
D
occurrence of $$P$$ in solid while $$N$$ in gaseous state at
room temperature.
Answer :
availability of vacant $$d$$ orbitals in $$P$$ but not in $$N$$
528. Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is a coloured gas?
A
$${N_2}O$$
B
$$NO$$
C
$${N_2}{O_5}$$
D
$$N{O_2}$$
Answer :
$$N{O_2}$$
529. Which of the following does not show electrical conduction?
A
Potassium
B
Graphite
C
Diamond
D
Sodium
Answer :
Diamond
530. When three parts of cone. $$HCl$$ and one part of cone. $$HN{O_3}$$ is mixed, a compound $$'X'$$ is formed. The correct option related to $$'X'$$ is
A
$$'X'$$ is known as aqua-regia
B
$$'X'$$ is used for dissolving gold
C
$$'X'$$ is used for decomposition of salts of weaker acids
D
both (A) and (B)
Answer :
both (A) and (B)