241. The first ionisation potential of aluminium is smaller than that of magnesium because
A
Atomic size of $$Al >$$ Atomic size of $$Mg.$$
B
Atomic size of $$Al <$$ Atomic size of $$Mg.$$
C
$$Al$$ has one electron in $$p$$ - orbital
D
None of these
Answer :
$$Al$$ has one electron in $$p$$ - orbital
242.
Part of the periodic table showing $$p$$ - block is depicted below. What are
the elements shown in the zig-zag boxes called? What is the nature of
the elements outside this boundary on the right side of the table?
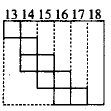
A
Transition elements, metalloids
B
Metalloids, non-metals
C
Metals, non-metals
D
Non-metals, noble gases
Answer :
Metalloids, non-metals
243. Which of the following is not the correct order for the stated property ?
A
$$Ba > Sr > Mg;$$ atomic radius
B
$$F > O > N:$$ first ionization enthalpy
C
$$Cl > F > I;$$ electron affinity
D
$$O > Se > Te;$$ electronegativity
Answer :
$$F > O > N:$$ first ionization enthalpy
244. Which statement is false?
A
Elements of group 16 are called chalcogens.
B
Elements of group 15 are all metalloids.
C
Elements of group 1 are alkali metals.
D
Elements of group 14 are neither strongly electronegative nor strongly electropositive.
Answer :
Elements of group 15 are all metalloids.
245. In a given energy level, the order of penetration effect of different orbitals is
A
$$f < d < p < s$$
B
$$s = p = d = f$$
C
$$s < p < d < f$$
D
$$p > s > d > f$$
Answer :
$$f < d < p < s$$
246. The ionisation of hydrogen atom would give rise to
A
hydride ion
B
hydronium ion
C
proton
D
hydroxyl ion
Answer :
proton