Question
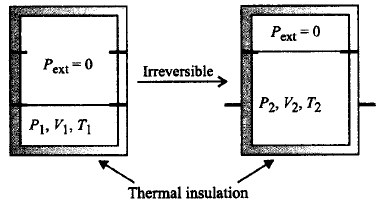
An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure $$ = {P_1},$$ volume $$ = {V_1}$$ and absolute temperature $$ = {T_1}$$ expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of gas are $${P_2},{V_2}$$ and $${T_2},$$ respectively. For this expansion,
An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure $$ = {P_1},$$ volume $$ = {V_1}$$ and absolute temperature $$ = {T_1}$$ expands irreversibly against zero external pressure, as shown in the diagram. The final internal pressure, volume and absolute temperature of gas are $${P_2},{V_2}$$ and $${T_2},$$ respectively. For this expansion,
A.
$$q = 0$$
B.
$${T_2} = {T_1}$$
C.
$${P_2}{V_2} = {P_1}{V_1}$$
D.
$${\text{all of these}}$$
Answer :
$${\text{all of these}}$$
Solution :
Since vessel is thermally insulated, i.e., the process is adiabatic hence, $$q = 0.$$ Also, $${P_{{\text{ext}}}} = 0,$$ hence $$w = 0$$
From 1st law of thermodynamics, $$\Delta U = q + w$$
$$\therefore \,\,\Delta U = 0$$ ( for ideal gas )
$$\therefore \,\,\Delta T = 0$$ or $${T_2} = {T_1}$$
[ $$\because $$ Internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature. ]
Applying ideal gas equation, $$PV = nRT$$
where $$n, R$$ and $$T$$ are constant. Then $${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$$
Since vessel is thermally insulated, i.e., the process is adiabatic hence, $$q = 0.$$ Also, $${P_{{\text{ext}}}} = 0,$$ hence $$w = 0$$
From 1st law of thermodynamics, $$\Delta U = q + w$$
$$\therefore \,\,\Delta U = 0$$ ( for ideal gas )
$$\therefore \,\,\Delta T = 0$$ or $${T_2} = {T_1}$$
[ $$\because $$ Internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature. ]
Applying ideal gas equation, $$PV = nRT$$
where $$n, R$$ and $$T$$ are constant. Then $${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$$