Releted MCQ Question on
Basic Physics >> Kinematics
Releted Question 1
A river is flowing from west to east at a speed of $$5$$ metres per minute. A man on the south bank of the river, capable of swimming at $$10$$ metres per minute in still water, wants to swim across the river in the shortest time. He should swim in a direction-
A.
Due north
B.
$${30^ \circ }$$ East of north
C.
$${30^ \circ }$$ West of north
D.
$${60^ \circ }$$ East of north
Releted Question 2
A boat which has a speed of $$5 km/hr$$ in still water crosses a river of width $$1 \,km$$ along the shortest possible path in $$15 \,minutes.$$ The velocity of the river water in $$km/hr$$ is-
A.
1
B.
3
C.
4
D.
$$\sqrt {41} $$
Releted Question 3
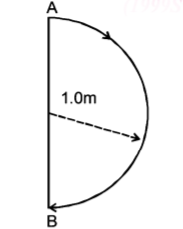
In $$1.0\,s,$$ a particle goes from point $$A$$ to point $$B,$$ moving in a semicircle of radius $$1.0 \,m$$ (see Figure). The magnitude of the average velocity-
In $$1.0\,s,$$ a particle goes from point $$A$$ to point $$B,$$ moving in a semicircle of radius $$1.0 \,m$$ (see Figure). The magnitude of the average velocity-
A.
$$3.14 \,m/s$$
B.
$$2.0 \,m/s$$
C.
$$1.0 \,m/s$$
D.
Zero
Releted Question 4
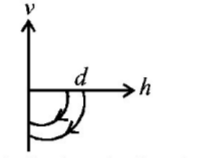
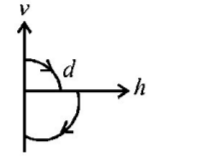
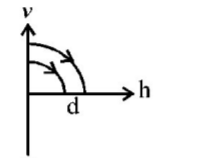
A ball is dropped vertically from a height $$d$$ above the ground. It hits the ground and bounces up vertically to a height $$\frac{d}{2}.$$ Neglecting subsequent motion and air resistance, its velocity $$v$$ varies with the height $$h$$ above the ground as-
A.

B.

C.
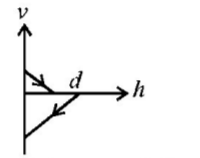

D.