Question
Two $$220\,V,100\,W$$ bulbs are connected first in series and then in parallel. Each time the combination is connected to a $$220\,V$$ AC supply line. The power drawn by the combination in each case respectively will be
A.
$$200\,W,150\,W$$
B.
$$50\,W,200\,W$$
C.
$$50\,W,100\,W$$
D.
$$100\,W,50\,W$$
Answer :
$$50\,W,200\,W$$
Solution :
Power $$P = 100\,W,$$ Voltage, $$V = 220\,V$$
$$\eqalign{ & P = \frac{{{V^2}}}{R} \cr & \therefore R = \frac{{{V^2}}}{P} = \frac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{100}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}\Omega \cr} $$
As both the bulb have same voltage and power so, resistance of bulbs will also be same.
Case I
When two bulbs are connected in series.
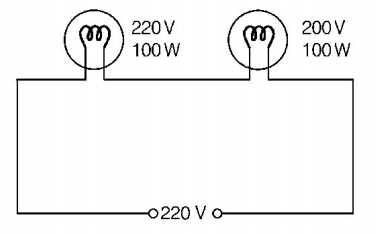
In series, $${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$$
$$ = \left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}} \right) \times 2$$
Hence, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{V^2}}}{{{R_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{\left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times 2} \right)}}$$
$$ = \frac{{100}}{2} = 50\,W$$
Case II
When two bulbs are connected in parallel.
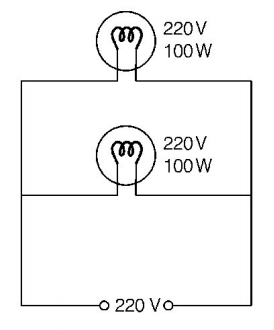
In parallel, $${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}} = \frac{{{{\left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}} \right)}^2}}}{{\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times 2}}$$
$${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times \frac{1}{2}$$
Hence, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{V^2}}}{{{R_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times \frac{1}{2}}}$$
$$ = 200\,W$$
Alternative
For series, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{P_1}{P_2}}}{{{P_1} + {P_2}}}$$
$$ = \frac{{100 \times 100}}{{200}} = 50\,W$$
For parallel, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$$
$$ = 100 + 100 = 200\,W$$
NOTE
Power equivalent of two or more resistance in series is given by $$\frac{1}{{{P_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{1}{{{P_1}}} + \frac{1}{{{P_2}}}$$ and for parallel combination $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$$
Power $$P = 100\,W,$$ Voltage, $$V = 220\,V$$
$$\eqalign{ & P = \frac{{{V^2}}}{R} \cr & \therefore R = \frac{{{V^2}}}{P} = \frac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{100}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}\Omega \cr} $$
As both the bulb have same voltage and power so, resistance of bulbs will also be same.
Case I
When two bulbs are connected in series.

In series, $${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$$
$$ = \left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}} \right) \times 2$$
Hence, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{V^2}}}{{{R_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{\left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times 2} \right)}}$$
$$ = \frac{{100}}{2} = 50\,W$$
Case II
When two bulbs are connected in parallel.

In parallel, $${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{R_1}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}} = \frac{{{{\left( {\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}}} \right)}^2}}}{{\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times 2}}$$
$${R_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times \frac{1}{2}$$
Hence, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{V^2}}}{{{R_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{{220 \times 220}}{{\frac{{220 \times 220}}{{100}} \times \frac{1}{2}}}$$
$$ = 200\,W$$
Alternative
For series, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = \frac{{{P_1}{P_2}}}{{{P_1} + {P_2}}}$$
$$ = \frac{{100 \times 100}}{{200}} = 50\,W$$
For parallel, $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$$
$$ = 100 + 100 = 200\,W$$
NOTE
Power equivalent of two or more resistance in series is given by $$\frac{1}{{{P_{{\text{eq}}}}}} = \frac{1}{{{P_1}}} + \frac{1}{{{P_2}}}$$ and for parallel combination $${P_{{\text{eq}}}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$$