Releted MCQ Question on
Heat and Thermodynamics >> Thermodynamics
Releted Question 1
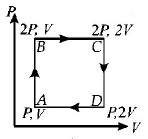
An ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cycle $$ABCDA$$ as shown in the $$P - V$$ diagram (see Fig.). The work done during the cycle is
An ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cycle $$ABCDA$$ as shown in the $$P - V$$ diagram (see Fig.). The work done during the cycle is
A.
$$PV$$
B.
$$2PV$$
C.
$$\frac{1}{2}PV$$
D.
zero
Releted Question 2
If one mole of a monatomic gas $$\left( {\gamma = \frac{5}{3}} \right)$$ is mixed with one mole of a diatomic gas $$\left( {\gamma = \frac{7}{5}} \right)$$ the value of $$\gamma $$ for mixture is
A.
1.40
B.
1.50
C.
1.53
D.
3.07
Releted Question 3
A closed compartment containing gas is moving with some acceleration in horizontal direction. Neglect effect of gravity. Then the pressure in the compartment is
A.
same everywhere
B.
lower in the front side
C.
lower in the rear side
D.
lower in the upper side
Releted Question 4
A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at temperature $$T.$$ Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is
A.
$$4\, RT$$
B.
$$15\, RT$$
C.
$$9\, RT$$
D.
$$11\, RT$$