Releted MCQ Question on
Electrostatics and Magnetism >> Electric Current
Releted Question 1
The temperature coefficient of resistance of a wire is 0.00125 per $$^ \circ C$$ At $$300\,K,$$ its resistance is $$1\,ohm.$$ This resistance of the wire will be $$2\,ohm$$ at.
A.
$$1154\,K$$
B.
$$1100\,K$$
C.
$$1400\,K$$
D.
$$1127\,K$$
Releted Question 2
A constant voltage is applied between the two ends of a uniform metallic wire. Some heat is developed in it. The heat developed is doubled if
A.
both the length and the radius of the wire are halved.
B.
both the length and the radius of the wire are doubled.
C.
the radius of the wire is doubled.
D.
the length of the wire is doubled.
Releted Question 3
The electrostatic field due to a point charge depends on the distance $$r$$ as $$\frac{1}{{{r^2}}}.$$ Indicate which of the following quantities shows same dependence on $$r.$$
A.
Intensity of light from a point source.
B.
Electrostatic potential due to a point charge.
C.
Electrostatic potential at a distance r from the centre of a charged metallic sphere. Given $$r$$ < radius of the sphere.
D.
None of these
Releted Question 4
The current $$i$$ in the circuit (see Fig) is
The current $$i$$ in the circuit (see Fig) is
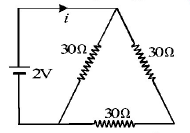
A.
$$\frac{1}{{45}}A$$
B.
$$\frac{1}{{15}}A$$
C.
$$\frac{1}{{10}}A$$
D.
$$\frac{1}{5}A$$