Question
For the given uniform square lamina $$ABCD,$$ whose centre is $$o,$$
For the given uniform square lamina $$ABCD,$$ whose centre is $$o,$$
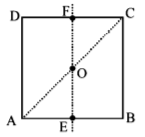
A.
$${I_{AC}} = \sqrt 2 {I_{EF}}$$
B.
$$\sqrt 2 {I_{AC}} = {I_{EF}}$$
C.
$${I_{AD}} = 3{I_{EF}}$$
D.
$${I_{AC}} = {I_{EF}}$$
Answer :
$${I_{AC}} = {I_{EF}}$$
Solution :
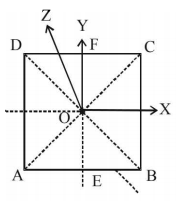
By the theorem of perpendicular axes,
$$\eqalign{ & {I_z} = {I_x} + {I_y} \cr & {\text{or}},\,\,{I_z} = 2{I_y} \cr & \left( {\because \,\,{I_x} = {I_y}{\text{ by symmetry of the figure}}} \right) \cr & \therefore {I_{EF}} = \frac{{{I_z}}}{2}\,\,.....(i) \cr} $$
Again, by the same theorem
$$\eqalign{ & {I_z} = {I_{AC}} + {I_{BD}} = 2{I_{AC}} \cr & \left( {\therefore \,{I_{AC}} = {I_{BD}}\,\,{\text{by symmetry of the figure}}} \right) \cr & \therefore {I_{AC}} = \frac{{{I_z}}}{2}\,\,.....(ii) \cr} $$
from (i) and (ii), we get $${I_{EF}} = {I_{AC}}$$

By the theorem of perpendicular axes,
$$\eqalign{ & {I_z} = {I_x} + {I_y} \cr & {\text{or}},\,\,{I_z} = 2{I_y} \cr & \left( {\because \,\,{I_x} = {I_y}{\text{ by symmetry of the figure}}} \right) \cr & \therefore {I_{EF}} = \frac{{{I_z}}}{2}\,\,.....(i) \cr} $$
Again, by the same theorem
$$\eqalign{ & {I_z} = {I_{AC}} + {I_{BD}} = 2{I_{AC}} \cr & \left( {\therefore \,{I_{AC}} = {I_{BD}}\,\,{\text{by symmetry of the figure}}} \right) \cr & \therefore {I_{AC}} = \frac{{{I_z}}}{2}\,\,.....(ii) \cr} $$
from (i) and (ii), we get $${I_{EF}} = {I_{AC}}$$