Releted MCQ Question on
Electrostatics and Magnetism >> Capacitors and Dielectrics
Releted Question 1
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance $$C$$ is connected to a battery and is charged to a potential difference $$V.$$ Another capacitor of capacitance $$2C$$ is similarly charged to a potential difference $$2V.$$ The charging battery is now disconnected and the capacitors are connected in parallel to each other in such a way that the positive terminal of one is connected to the negative terminal of the other. The final energy of the configuration is
A.
zero
B.
$$\frac{3}{2}C{V^2}$$
C.
$$\frac{{25}}{6}C{V^2}$$
D.
$$\frac{9}{2}C{V^2}$$
Releted Question 2
Two identical metal plates are given positive charges $${Q_1}$$ and $${Q_2}\left( { < {Q_1}} \right)$$ respectively. If they are now brought close together to form a parallel plate capacitor with capacitance $$C,$$ the potential difference between them is
A.
$$\frac{{\left( {{Q_1} + {Q_2}} \right)}}{{2C}}$$
B.
$$\frac{{\left( {{Q_1} + {Q_2}} \right)}}{C}$$
C.
$$\frac{{\left( {{Q_1} - {Q_2}} \right)}}{C}$$
D.
$$\frac{{\left( {{Q_1} - {Q_2}} \right)}}{{2C}}$$
Releted Question 3
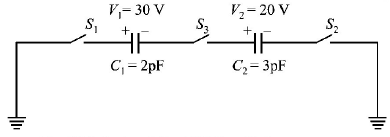
For the circuit shown in Figure, which of the following statements is true?
For the circuit shown in Figure, which of the following statements is true?
A.
With $${S_1}$$ closed $${V_1} = 15\,V,{V_2} = 20\,V$$
B.
With $${S_3}$$ closed $${V_1} = {V_2} = 25\,V$$
C.
With $${S_1}$$ and $${S_2}$$ closed, $${V_1} = {V_2} = 0$$
D.
With $${S_1}$$ and $${S_3}$$ closed, $${V_1} = 30\,V,{V_2} = 20\,V$$
Releted Question 4
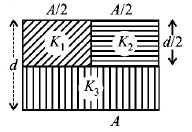
A parallel plate capacitor of area $$A,$$ plate separation $$d$$ and capacitance $$C$$ is filled with three different dielectric materials having dielectric constants $${k_1},{k_2}$$ and $${k_3}$$ as shown. If a single dielectric material is to be used to have the same capacitance $$C$$ in this capacitor, then its dielectric constant $$k$$ is given by
A parallel plate capacitor of area $$A,$$ plate separation $$d$$ and capacitance $$C$$ is filled with three different dielectric materials having dielectric constants $${k_1},{k_2}$$ and $${k_3}$$ as shown. If a single dielectric material is to be used to have the same capacitance $$C$$ in this capacitor, then its dielectric constant $$k$$ is given by
A.
$$\frac{1}{K} = \frac{1}{{{K_1}}} + \frac{1}{{{K_2}}} + \frac{1}{{2{K_3}}}$$
B.
$$\frac{1}{K} = \frac{1}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}} + \frac{1}{{2{K_3}}}$$
C.
$$K = \frac{{{K_1}{K_2}}}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}} + 2{K_3}$$
D.
$$K = {K_1} + {K_2} + 2{K_3}$$