Question
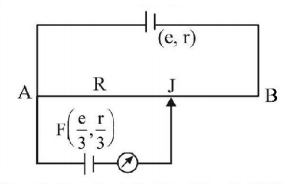
A potentiometer arrangement is shown in fig. The driver cell has emf $$e$$ and internal resistance $$r.$$ The resistance of potentiometer wire $$AB$$ is $$R.$$ $$F$$ is the cell of $$em\,\frac{e}{3}$$ and internal resistance $$\frac{r}{3}.$$ Balance point $$\left( J \right)$$ can be obtained for all finite values of
A potentiometer arrangement is shown in fig. The driver cell has emf $$e$$ and internal resistance $$r.$$ The resistance of potentiometer wire $$AB$$ is $$R.$$ $$F$$ is the cell of $$em\,\frac{e}{3}$$ and internal resistance $$\frac{r}{3}.$$ Balance point $$\left( J \right)$$ can be obtained for all finite values of
A.
$$R > \frac{r}{2}$$
B.
$$R < \frac{r}{2}$$
C.
$$R > \frac{r}{3}$$
D.
$$R < \frac{r}{3}$$
Answer :
$$R > \frac{r}{2}$$
Solution :
Current in $$AB = I = \frac{e}{{R + r}}$$
potential difference across $$AB = IR = \frac{{eR}}{{R + r}}$$
To obtain balanced point,
$$\frac{{eR}}{{R + r}} > \frac{e}{3}\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,R > \frac{r}{2}$$
Current in $$AB = I = \frac{e}{{R + r}}$$
potential difference across $$AB = IR = \frac{{eR}}{{R + r}}$$
To obtain balanced point,
$$\frac{{eR}}{{R + r}} > \frac{e}{3}\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,R > \frac{r}{2}$$