Question
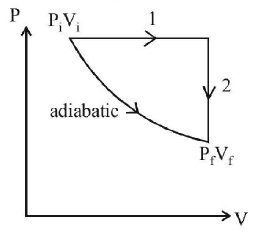
A gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a movable frictionless piston. Its initial thermodynamic state at pressure $${P_i} = {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$ and volume $${V_i} = {10^{ - 3}}{m^3}$$ changes to a final state at $${P_f} = \left( {\frac{1}{{32}}} \right) \times {10^5}$$ $$Pa$$ and $${V_f} = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}{m^3}$$ in an adiabatic quasi - static process, such that $${P^3}{V^5}$$ = constant. Consider another thermodynamic process that brings the system from the same initial state to the same final state in two steps: an isobaric expansion at $${P_i}$$ followed by an isochoric (isovolumetric) process at volume $${V_f}.$$ The amount of heat supplied to the system in the two - step process is approximately
A.
$$112\, J$$
B.
$$294\, J$$
C.
$$588\, J$$
D.
$$813\, J$$
Answer :
$$588\, J$$
Solution :
$$\eqalign{ & {P^3}{V^5} = {\text{constant}} \cr & \Rightarrow \,\,P{V^{\frac{5}{3}}} = {\text{constant}} \cr & \Rightarrow \,\,\gamma = \frac{5}{3} \cr} $$
⇒ monoatomic gas
For adiabatic process
$$\eqalign{ & W = \frac{{{P_f}{V_f} - {P_i}{V_i}}}{{1 - \gamma }} \cr & = \frac{{\frac{1}{{32}} \times {{10}^5} \times 8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} - {{10}^5} \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{1 - \frac{5}{3}}} \cr & \therefore \,\,W = \frac{{25 - 100}}{{\frac{{\left( {3 - 5} \right)}}{3}}} \cr & = \frac{{75 \times 3}}{2} \cr & = 112.5\,J \cr} $$
From first law of thermodynamics $$q = \Delta U + w$$
$$\eqalign{ & \therefore \,\,\Delta U = - w \cr & \therefore \,\,\Delta U = - 112.5\,J \cr} $$
Now applying first law of thermodynamics for process 1 & 2 and adding $${q_1} + {q_2} = \Delta U + {P_i}\left( {{V_f} - {V_i}} \right)$$
$$\eqalign{ & = - 112.5 + {10^5}\left( {8 - 1} \right) \times {10^{ - 3}} \cr & = 587.55 \cr} $$
$$\eqalign{ & {P^3}{V^5} = {\text{constant}} \cr & \Rightarrow \,\,P{V^{\frac{5}{3}}} = {\text{constant}} \cr & \Rightarrow \,\,\gamma = \frac{5}{3} \cr} $$
⇒ monoatomic gas
For adiabatic process

$$\eqalign{ & W = \frac{{{P_f}{V_f} - {P_i}{V_i}}}{{1 - \gamma }} \cr & = \frac{{\frac{1}{{32}} \times {{10}^5} \times 8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} - {{10}^5} \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{1 - \frac{5}{3}}} \cr & \therefore \,\,W = \frac{{25 - 100}}{{\frac{{\left( {3 - 5} \right)}}{3}}} \cr & = \frac{{75 \times 3}}{2} \cr & = 112.5\,J \cr} $$
From first law of thermodynamics $$q = \Delta U + w$$
$$\eqalign{ & \therefore \,\,\Delta U = - w \cr & \therefore \,\,\Delta U = - 112.5\,J \cr} $$
Now applying first law of thermodynamics for process 1 & 2 and adding $${q_1} + {q_2} = \Delta U + {P_i}\left( {{V_f} - {V_i}} \right)$$
$$\eqalign{ & = - 112.5 + {10^5}\left( {8 - 1} \right) \times {10^{ - 3}} \cr & = 587.55 \cr} $$