Releted MCQ Question on
Heat and Thermodynamics >> Radiation
Releted Question 1
Two metallic spheres $${S_1}$$ and $${S_2}$$ are made of the same material and have got identical surface finish. The mass of $${S_1}$$ is thrice that of $${S_2}.$$ Both the spheres are heated to the same high temperature and placed in the same room having lower temperature but are thermally insulated from each other. The ratio of the initial rate of cooling of $${S_1}$$ to that of $${S_2}$$ is
A.
$$\frac{1}{3}$$
B.
$${\frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}}$$
C.
$${\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{1}}$$
D.
$${\left( {\frac{1}{3}} \right)^{\frac{1}{3}}}$$
Releted Question 2
A spherical black body with a radius of $$12\,cm$$ radiates 450 $$W$$ power at 500 $$K.$$ if the radius were halved and the temperature doubled, the power radiated in watt would be
A.
225
B.
450
C.
900
D.
1800
Releted Question 3
A spherical black body with a radius of $$12\,cm$$ radiates $$450\,W$$ power at 500 $$K.$$ If the radius were halved and the temperature doubled, the power radiated in watt would be
A.
225
B.
450
C.
900
D.
1800
Releted Question 4
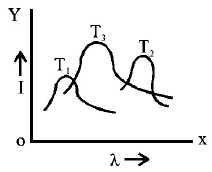
The plots of intensity versus wavelength for three black bodies at temperature $${T_1},$$ $${T_2}$$ and $${T_3}$$ respectively are as shown. Their temperatures are such that
The plots of intensity versus wavelength for three black bodies at temperature $${T_1},$$ $${T_2}$$ and $${T_3}$$ respectively are as shown. Their temperatures are such that
A.
$${T_1} > {T_2} > {T_3}$$
B.
$${T_1} > {T_3} > {T_2}$$
C.
$${T_2} > {T_3} > {T_1}$$
D.
$${T_3} > {T_2} > {T_1}$$