Releted MCQ Question on
Heat and Thermodynamics >> Calorimetry
Releted Question 1
A block of ice at $$ - {10^ \circ }C$$ is slowly heated and converted to steam at $${100^ \circ }C.$$ Which of the following curves represents the phenomenon qualitatively?
A.
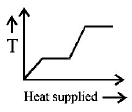

B.
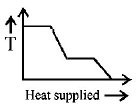

C.
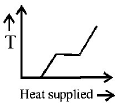

D.


Releted Question 2
An ideal Black - body at room temperature is thrown into a furnace. It is observed that
A.
initially it is the darkest body and at later times the brightest
B.
it is the darkest body at all times
C.
it cannot be distinguished at all times
D.
initially it is the darkest body and at later times it cannot be distinguished
Releted Question 3
The graph, shown in the adjacent diagram, represents the variation of temperature $$(T)$$ of two bodies, $$x$$ and $$y$$ having same surface area, with time $$(t)$$ due to the emission of radiation. Find the correct relation between the emissivity and absorptivity power of the two bodies
The graph, shown in the adjacent diagram, represents the variation of temperature $$(T)$$ of two bodies, $$x$$ and $$y$$ having same surface area, with time $$(t)$$ due to the emission of radiation. Find the correct relation between the emissivity and absorptivity power of the two bodies
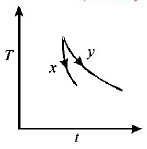
A.
$${E_x} > {E_y}\,\,\& \,\,{a_x} < {a_y}$$
B.
$${E_x} < {E_y}\,\,\& \,\,{a_x} > {a_y}$$
C.
$${E_x} > {E_y}\,\,\& \,\,{a_x} > {a_y}$$
D.
$${E_x} < {E_y}\,\,\& \,\,{a_x} < {a_y}$$
Releted Question 4
$$2\,kg$$ of ice at $$ - {20^ \circ }C$$ is mixed with $$5\,kg$$ of water at $${20^ \circ }C$$ in an insulating vessel having a negligible heat capacity. Calculate the final mass of water remaining in the container. It is given that the specific heats of water & ice are $$1\,k\,cal/kg/{\,^ \circ }C\,\,\& \,\,0.5\,k\,cal/kg/{\,^ \circ }C$$ while the latent heat of fusion of ice is $$80\,k\,cal/kg$$
A.
$$7\,kg$$
B.
$$6\,kg$$
C.
$$4\,kg$$
D.
$$2\,kg$$