Question
Two metal wires of identical dimensions are connected in series. If $${\sigma _1}$$ and $${\sigma _2}$$ are the conductivities of the metal wires respectively, the effective conductivity of the combination is
A.
$$\frac{{2{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}$$
B.
$$\frac{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}{{2{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}$$
C.
$$\frac{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}$$
D.
$$\frac{{{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{2{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}$$
Solution :
Net resistance of a metal wire having resistivity $$\rho ,$$ we have
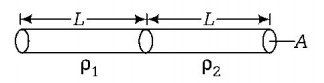
$$\eqalign{ & {R_1} = {\rho _1}\frac{L}{A} \cr & {\text{Similarly,}}\,{R_2} = {\rho _2}\frac{L}{A} \cr & {\text{Then, net effective resistance of two metal wires,}} \cr & {R_{{\text{eq}}}} = {R_1} + {R_2} \Rightarrow \rho \frac{{2L}}{A} = {\rho _1}\frac{L}{A} + {\rho _2}\frac{L}{A} \cr & \Rightarrow 2\rho = {\rho _1} + {\rho _2} \cr & {\text{As, conductivity}}\,\sigma = \frac{1}{\rho },\,{\text{we have}} \cr & \frac{2}{\sigma } = \frac{1}{{{\sigma _1}}} + \frac{1}{{{\sigma _2}}} \Rightarrow \frac{2}{\sigma } = \frac{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}} \cr & \Rightarrow {\text{Net effective conductivity of combined wires,}} \cr & \sigma = \frac{{2{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}} \cr} $$
Net resistance of a metal wire having resistivity $$\rho ,$$ we have

$$\eqalign{ & {R_1} = {\rho _1}\frac{L}{A} \cr & {\text{Similarly,}}\,{R_2} = {\rho _2}\frac{L}{A} \cr & {\text{Then, net effective resistance of two metal wires,}} \cr & {R_{{\text{eq}}}} = {R_1} + {R_2} \Rightarrow \rho \frac{{2L}}{A} = {\rho _1}\frac{L}{A} + {\rho _2}\frac{L}{A} \cr & \Rightarrow 2\rho = {\rho _1} + {\rho _2} \cr & {\text{As, conductivity}}\,\sigma = \frac{1}{\rho },\,{\text{we have}} \cr & \frac{2}{\sigma } = \frac{1}{{{\sigma _1}}} + \frac{1}{{{\sigma _2}}} \Rightarrow \frac{2}{\sigma } = \frac{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}} \cr & \Rightarrow {\text{Net effective conductivity of combined wires,}} \cr & \sigma = \frac{{2{\sigma _1}{\sigma _2}}}{{{\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2}}} \cr} $$
