Question
The shortest distance between the skew lines $${l_1}:\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {{a_1}} + \lambda \overrightarrow {{b_1}} ,\,{l_2}:\overrightarrow r = \overrightarrow {{a_2}} + \mu \overrightarrow {{b_2}} {\text{ is :}}$$
A.
$$\frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
B.
$$\frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{a_2}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
C.
$$\frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{a_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_1}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
D.
$$\frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_1}} - \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right|}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
Solution :
Let $$PQ$$ be the shortest distance vector between $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}.$$
Now, $${l_1}$$ passes through $${A_1}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right)$$ and is parallel to $${\overrightarrow {{b_1}} }$$ and $${l_2}$$ passes through $${A_2}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right)$$ and is parallel to $${\overrightarrow {{b_2}} }.$$
Since, $$PQ$$ is perpendicular to both $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}$$ it is parallel to $$\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} .$$
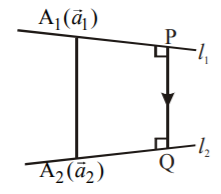
Let $${\hat n}$$ be the unit vector along $$PQ.$$
Then, $$\hat n = \frac{{\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} }}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
Let $$d$$ be the shortest distance between the given lines $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}.$$
$$\overrightarrow {\left| {PQ} \right|} = d$$ and $$\overrightarrow {\left| {PQ} \right|} = d\,\hat n$$
Next $$PQ$$ being the line of shortest distance between $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}$$ is the projection of the line joining the points $${A_1}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right)$$ and $${A_2}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right)$$ on $${\hat n}$$ ;
$$\left| {\overrightarrow {PQ} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {{A_1}} \overrightarrow {{A_2}} .\hat n} \right| \Rightarrow d = \frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
Let $$PQ$$ be the shortest distance vector between $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}.$$
Now, $${l_1}$$ passes through $${A_1}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right)$$ and is parallel to $${\overrightarrow {{b_1}} }$$ and $${l_2}$$ passes through $${A_2}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right)$$ and is parallel to $${\overrightarrow {{b_2}} }.$$
Since, $$PQ$$ is perpendicular to both $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}$$ it is parallel to $$\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} .$$

Let $${\hat n}$$ be the unit vector along $$PQ.$$
Then, $$\hat n = \frac{{\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} }}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$
Let $$d$$ be the shortest distance between the given lines $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}.$$
$$\overrightarrow {\left| {PQ} \right|} = d$$ and $$\overrightarrow {\left| {PQ} \right|} = d\,\hat n$$
Next $$PQ$$ being the line of shortest distance between $${l_1}$$ and $${l_2}$$ is the projection of the line joining the points $${A_1}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right)$$ and $${A_2}\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} } \right)$$ on $${\hat n}$$ ;
$$\left| {\overrightarrow {PQ} } \right| = \left| {\overrightarrow {{A_1}} \overrightarrow {{A_2}} .\hat n} \right| \Rightarrow d = \frac{{\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow {{a_2}} - \overrightarrow {{a_1}} } \right).\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}{{\left| {\overrightarrow {{b_1}} \times \overrightarrow {{b_2}} } \right|}}$$