Question
The line $$x + y = a$$ meets the axes of $$x$$ and $$y$$ at $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively. A $$\Delta AMN$$ is inscribed in the $$\Delta OAB,\,O$$ being the origin, with right angle at $$N.\,M$$ and $$N$$ lie respectively on $$OB$$ and $$AB.$$ If the area of the $$\Delta AMN$$ is $$\frac{3}{8}$$ of the area of the $$\Delta OAB,$$ then $$\frac{{AN}}{{BN}}$$ is equal to :
A.
$$\frac{1}{3}$$
B.
$$\frac{1}{3},\,3$$
C.
$$\frac{2}{3},\,3$$
D.
$$3$$
Answer :
$$3$$
Solution :
Let $$\frac{{AN}}{{BN}} = \lambda .$$
Then, the coordinates of $$N$$ are $$\left( {\frac{a}{{1 + \lambda }},\,\frac{{\lambda a}}{{1 + \lambda }}} \right).$$
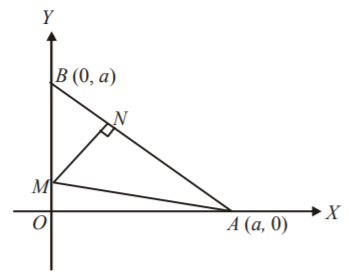
Where $$\left( {a,\,0} \right)$$ and $$\left( {0,\,a} \right)$$ are the coordinates of $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively. Now, equation of $$MN$$ perpendicular to $$AB$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & y - \frac{{\lambda a}}{{1 + \lambda }} = x - \frac{a}{{1 + \lambda }} \cr & \Rightarrow x - y = \frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{1 + \lambda }}a \cr} $$
So, the coordinates of $$M$$ are $$\left( {0,\,\frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{1 + \lambda }}a} \right)$$
Therefore, area of the $$\Delta AMN$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & = \frac{1}{2}\left| {\left[ {a\left( {\frac{{ - a}}{{\lambda + 1}}} \right) + \frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}}{a^2}} \right]} \right| \cr & = \frac{{\lambda {a^2}}}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}} \cr} $$
Also, area of $$\Delta OAB = \frac{{{a^2}}}{2}$$
So, that according to the given condition
$$\eqalign{ & \frac{{\lambda {a^2}}}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}} = \frac{3}{8}.\frac{1}{2}{a^2} \cr & \Rightarrow 3{\lambda ^2} - 10\lambda + 3 = 0 \cr & \Rightarrow \lambda = 3{\text{ or }}\lambda = \frac{1}{3} \cr} $$
For $$\lambda = \frac{1}{3},\,M$$ lies outside the segment $$OB$$ and hence the required value of $$\lambda $$ is $$3.$$
Let $$\frac{{AN}}{{BN}} = \lambda .$$
Then, the coordinates of $$N$$ are $$\left( {\frac{a}{{1 + \lambda }},\,\frac{{\lambda a}}{{1 + \lambda }}} \right).$$

Where $$\left( {a,\,0} \right)$$ and $$\left( {0,\,a} \right)$$ are the coordinates of $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively. Now, equation of $$MN$$ perpendicular to $$AB$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & y - \frac{{\lambda a}}{{1 + \lambda }} = x - \frac{a}{{1 + \lambda }} \cr & \Rightarrow x - y = \frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{1 + \lambda }}a \cr} $$
So, the coordinates of $$M$$ are $$\left( {0,\,\frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{1 + \lambda }}a} \right)$$
Therefore, area of the $$\Delta AMN$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & = \frac{1}{2}\left| {\left[ {a\left( {\frac{{ - a}}{{\lambda + 1}}} \right) + \frac{{1 - \lambda }}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}}{a^2}} \right]} \right| \cr & = \frac{{\lambda {a^2}}}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}} \cr} $$
Also, area of $$\Delta OAB = \frac{{{a^2}}}{2}$$
So, that according to the given condition
$$\eqalign{ & \frac{{\lambda {a^2}}}{{{{\left( {1 + \lambda } \right)}^2}}} = \frac{3}{8}.\frac{1}{2}{a^2} \cr & \Rightarrow 3{\lambda ^2} - 10\lambda + 3 = 0 \cr & \Rightarrow \lambda = 3{\text{ or }}\lambda = \frac{1}{3} \cr} $$
For $$\lambda = \frac{1}{3},\,M$$ lies outside the segment $$OB$$ and hence the required value of $$\lambda $$ is $$3.$$