Question
The equation of the locus of the middle point of a chord of the circle $${x^2} + {y^2} = 2\left( {x + y} \right)$$ such that the pair of lines joining the origin to the point of intersection of the chord and the circle are equally inclined to the $$x$$-axis is :
A.
$$x + y = 2$$
B.
$$x - y = 2$$
C.
$$2x - y = 1$$
D.
none of these
Answer :
$$x + y = 2$$
Solution :
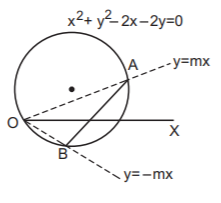
Solving $$y = mx$$ and $${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 2y = 0,$$ we get
$$\eqalign{ & {x^2} + {m^2}{x^2} - 2x - 2mx = 0 \cr & \Rightarrow \,x = 0,\,\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr} $$
Similarly, solving $$y = - mx$$ and the equation of the circle, we get
$$\eqalign{ & x = 0,\,\frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr & \therefore \,A = \left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\frac{{2m\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right)\,{\text{and }}B = \left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\frac{{ - 2m\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right) \cr} $$
Let the middle point of $$AB$$ be $$\left( {\alpha ,\,\beta } \right).$$ Then
$$\eqalign{ & \alpha = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} + \frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right){\text{ and }}\beta = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\frac{{2m\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} + \frac{{ - 2m\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right) \cr & \therefore \,\,\alpha = \frac{2}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\beta = \frac{{2{m^2}}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr} $$
Eliminating m from these, $$\alpha + \beta = 2.$$

Solving $$y = mx$$ and $${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 2y = 0,$$ we get
$$\eqalign{ & {x^2} + {m^2}{x^2} - 2x - 2mx = 0 \cr & \Rightarrow \,x = 0,\,\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr} $$
Similarly, solving $$y = - mx$$ and the equation of the circle, we get
$$\eqalign{ & x = 0,\,\frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr & \therefore \,A = \left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\frac{{2m\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right)\,{\text{and }}B = \left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\frac{{ - 2m\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right) \cr} $$
Let the middle point of $$AB$$ be $$\left( {\alpha ,\,\beta } \right).$$ Then
$$\eqalign{ & \alpha = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\frac{{2\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} + \frac{{2\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right){\text{ and }}\beta = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\frac{{2m\left( {1 + m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}} + \frac{{ - 2m\left( {1 - m} \right)}}{{1 + {m^2}}}} \right) \cr & \therefore \,\,\alpha = \frac{2}{{1 + {m^2}}},\,\beta = \frac{{2{m^2}}}{{1 + {m^2}}} \cr} $$
Eliminating m from these, $$\alpha + \beta = 2.$$