11. A metal surface is illuminated by light of two different wavelengths $$248\,nm$$ and $$310\,nm.$$ The maximum speeds of the photoelectrons corresponding to these wavelengths are $${u_1}$$ and $${u_2},$$ respectively. If the ratio $${u_1}:{u_2} = 2:1$$ and $$hc = 1240\,eV\,nm$$ the work function of the metal is nearly
A
$$3.7\,eV$$
B
$$3.2\,eV$$
C
$$2.8\,eV$$
D
$$2.5\,eV$$
Answer :
$$3.7\,eV$$
12.
The intensity of X-rays from a Coolidge tube is plotted
against wavelength $$\lambda $$ as shown in the figure. The minimum wavelength found is $${\lambda _C}$$ and the wavelength of the $${K_\alpha }$$ line is $${\lambda _K}.$$ As the accelerating voltage is increased
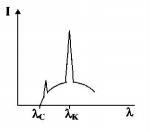
A
$${\lambda _K} - {\lambda _C}$$ increases
B
$${\lambda _K} - {\lambda _C}$$ decreases
C
$${\lambda _K}$$ increases
D
$${\lambda _K}$$ decreases
Answer :
$${\lambda _K} - {\lambda _C}$$ increases
13. Which one of the following statements is WRONG in the context of X-rays generated from a X-ray tube?
A
Wavelength of characteristic X-rays decreases when the atomic number of the target increases.
B
Cut-off wavelength of the continuous X-rays depends on the atomic number of the target
C
Intensity of the characteristic X-rays depends on the electrical power given to the X-ray tube
D
Cut-off wavelength of the continuous X-rays depends on the energy of the electrons in the X-ray tube
Answer :
Cut-off wavelength of the continuous X-rays depends on the atomic number of the target
14. A pulse of light of duration $$100\,ns$$ is absorbed completely by a small object initially at rest. Power of the pulse is $$30\,mW$$ and the speed of light is $$3 \times {10^8}m{s^{ - 1}}.$$ The final momentum of the object is
A
$$0.3 \times {10^{ - 17}}kg\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$1.0 \times {10^{ - 17}}kg\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$3.0 \times {10^{ - 17}}kg\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$9.0 \times {10^{ - 17}}kg\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$1.0 \times {10^{ - 17}}kg\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$
15. The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is $$5k\,V$$ and the current through it is 3.2$$mA.$$ Then the number of electrons striking the target per second is
A
$$2 \times {10^{16}}$$
B
$$5 \times {10^{6}}$$
C
$$1 \times {10^{17}}$$
D
$$4 \times {10^{15}}$$
Answer :
$$2 \times {10^{16}}$$
16. The time taken by a photoelectron to come out after the photon strikes is approximately
A
$${10^{ - 4}}s$$
B
$${10^{ - 10}}s$$
C
$${10^{ - 16}}s$$
D
$${10^{ - 1}}s$$
Answer :
$${10^{ - 10}}s$$
17. A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency $$50\,MHz$$ travels in free space along the positive $$x$$-direction. At a particular point in space and time, $$\vec E = 6.3\hat j\,V/m.$$ The corresponding magnetic field $${\vec B},$$ at that point will be:
A
$$18.9 \times {10^{ - 8}}$$
B
$$2.1 \times {10^{ - 8}}$$
C
$$6.3 \times {10^{ - 8}}$$
D
$$18.9 \times {10^8}$$
Answer :
$$2.1 \times {10^{ - 8}}$$
18. A photon collides with a stationary hydrogen atom in ground state inelastically. Energy of the colliding photon is $$10.2\,eV.$$ After a time interval of the order of micro second another photon collides with same hydrogen atom inelastically with an energy of $$15\,eV.$$ What will be observed by the detector?
A
One photon of energy $$10.2\,eV$$ and an electron of energy $$1.4\,eV$$
B
2 photon of energy of $$1.4\,eV$$
C
2 photon of energy $$10.2\,eV$$
D
One photon of energy $$10.2\,eV$$ and another photon of $$14\,eV$$
Answer :
One photon of energy $$10.2\,eV$$ and an electron of energy $$1.4\,eV$$
19. In amplitude modulation, sinusoidal carrier frequency used is denoted by $${\omega _c}$$ and the signal frequency is denoted by $${\omega _m}.$$ The bandwidth $$\left( {\Delta {\omega _m}} \right)$$ of the signal is such that $$\Delta {\omega _m} < {\omega _c}.$$ Which of the following frequencies is not contained in the modulated wave ?
A
$${\omega _m} + {\omega _c}$$
B
$${\omega _c} - {\omega _m}$$
C
$${\omega _m}$$
D
$${\omega _c}$$
Answer :
$${\omega _m}$$
20. The threshold frequency for a metallic surface corresponds to an energy of $$6.2\,eV$$ and the stopping potential for a radiation incident on this surface is $$5\,V.$$ The incident radiation lies in
A
ultra-violet region
B
infra-red region
C
visible region
D
X-ray region
Answer :
ultra-violet region