41. In a region, steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields are present. These two fields are parallel to each other. A charged particle is released from rest in this region. The path of the particle will be a
A
helix
B
straight line
C
ellipse
D
circle
Answer :
straight line
42. A current $$i$$ ampere flows along an infinitely long straight thin walled tube, then the magnetic induction at any point inside the tube is
A
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}.\frac{{2i}}{r}\,{\text{tesla}}$$
B
zero
C
infinite
D
$$\frac{{2i}}{r}\,{\text{tesla}}$$
Answer :
zero
43. A wire carries a current. Maintaining the same current it is bent first to form a circular plane coil of one turn which produces a magnetic field $$B$$ at the centre of the coil. The same length is now bent more sharply to give a double loop of smaller radius. The magnetic field at the centre of the double loop, caused by the same current is
A
$$4B$$
B
$$\frac{B}{4}$$
C
$$\frac{B}{2}$$
D
$$2B$$
Answer :
$$4B$$
44. A long straight wire along the $$Z$$-axis carries a current $$I$$ in the negative $$Z$$-direction. The magnetic vector field $$\overrightarrow B $$ at a point having coordinates $$\left( {x,{\text{ }}y} \right)$$ in the $$Z = 0$$ plane is
A
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}I\left( {y\hat i - x\hat j} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)}}$$
B
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}I\left( {x\hat i + y\hat j} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)}}$$
C
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}I\left( {x\hat j - y\hat i} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)}}$$
D
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}I\left( {x\hat i - y\hat j} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{{\mu _0}I\left( {y\hat i - x\hat j} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)}}$$
45. A particle of mass $$m$$ and charge $$g$$ moves with a constant velocity $$v$$ along the positive $$x$$ -direction. It enters a region containing a uniform magnetic field $$B$$ directed along the negative $$z$$ -direction, extending from $$x = a$$ to $$x = b.$$ The minimum value of $$v$$ required so that the particle can just enter the region $$x > b$$ is
A
$$\frac{{qbB}}{m}$$
B
$$\frac{{q\left( {b - a} \right)B}}{m}$$
C
$$\frac{{qaB}}{m}$$
D
$$\frac{{q\left( {b + a} \right)B}}{m}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{q\left( {b - a} \right)B}}{m}$$
46.
A loop carrying current $$I$$ lies in the $$x - y$$ plane as shown in the figure. The unit vector $${\hat k}$$ is coming out of the plane of the paper. The magnetic moment of the current loop is
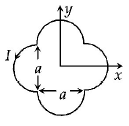
A
$${a^2}I\hat k$$
B
$$\left( {\frac{\pi }{2} + 1} \right){a^2}I\hat k$$
C
$$ - \left( {\frac{\pi }{2} + 1} \right){a^2}I\hat k$$
D
$$\left( {2\pi + 1} \right){a^2}I\hat k$$
Answer :
$$\left( {\frac{\pi }{2} + 1} \right){a^2}I\hat k$$
47. Two electron beams having their velocities in the ratio $$1:2$$ are subjected to identical magnetic fields acting at right angles to the direction of motion of electron beams. The ratio of deflection produced is:
A
$$2:1$$
B
$$1:2$$
C
$$4:1$$
D
$$1:4$$
Answer :
$$1:2$$
48. A charged particle with charge $$q$$ enters a region of constant, uniform and mutually orthogonal fields $$\overrightarrow E $$ and $$\overrightarrow B $$ with a velocity $$\overrightarrow v $$ perpendicular to both $$\overrightarrow E $$ and $$\overrightarrow B ,$$ and comes out without any change in magnitude or direction of $$\overrightarrow v .$$ Then
A
$$\overrightarrow v = \overrightarrow B \times \frac{{\overrightarrow E }}{{{E^2}}}$$
B
$$\overrightarrow v = \overrightarrow E \times \frac{{\overrightarrow B }}{{{B^2}}}$$
C
$$\overrightarrow v = \overrightarrow B \times \frac{{\overrightarrow E }}{{{B^2}}}$$
D
$$\overrightarrow v = \overrightarrow E \times \frac{{\overrightarrow B }}{{{E^2}}}$$
Answer :
$$\overrightarrow v = \overrightarrow E \times \frac{{\overrightarrow B }}{{{B^2}}}$$
49. A charged particle is released from rest in a region of steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields which are parallel to each other. The particle will move in a
A
straight line
B
circle
C
helix
D
cycloid
Answer :
straight line
50. A microammeter has a resistance of $$100\,\Omega $$ and full scale range of $$50\,\mu A.$$ It can be used as a voltmeter or as a higher range ammeter provided a resistance is added to it. Pick the correct range and resistance combination
A
$$50\,V$$ range with $$10\,k\Omega $$ resistance in series
B
$$10\,V$$ range with $$200\,k\Omega $$ resistance in series
C
$$10\,mA$$ range with $$1\,\Omega $$ resistance in parallel
D
$$10\,mA$$ range with $$0.1\,\Omega $$ resistance in parallel
Answer :
$$10\,V$$ range with $$200\,k\Omega $$ resistance in series


