51. Which of the following has the highest nucleophilicity ?
A
$${F^ - }$$
B
$$O{H^ - }$$
C
$$CH_3^ - $$
D
$$NH_2^ - $$
Answer :
$$CH_3^ - $$
52. The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is :
A
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\, \\
C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
B
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}} \\
|
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-C-}}}\,OH\]
C
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
D
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
|\,\,\,\,\, \\
OH\,\,
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-CH-}}\,C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}\]
Answer :
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}} \\
|
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-C-}}}\,OH\]
54.
The correct stability order for the following species is

A
(II) > (IV) > (I) > (III)
B
(I) > (II) > (III) > (IV)
C
(II) > (I) > (IV) > (III)
D
(I) > (III) > (II) > (IV)
Answer :
(I) > (III) > (II) > (IV)
55.
The IUPAC name of  is
is
A
3, 4-dimethylpentanoyl chloride
B
1-chloro-1-oxo-2, 3-dimethylpentane
C
2-ethyl-3-methylbutanoyl chloride
D
2, 3-dimethyl pentanoyl chloride
Answer :
2, 3-dimethyl pentanoyl chloride
56. The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is
A
$$ - H < - C{H_3} < - {C_2}{H_5} < - {C_3}{H_7}$$
B
$$ - H > - C{H_3} > - {C_2}{H_5} > - {C_3}{H_7}$$
C
$$ - H < - {C_2}{H_5} < - C{H_3} < - {C_3}{H_7}$$
D
$$ - H > - {C_2}{H_5} > - C{H_3} > - {C_3}{H_7}$$
Answer :
$$ - H < - C{H_3} < - {C_2}{H_5} < - {C_3}{H_7}$$
57. Which of the following represents the correct order of stability of the given carbocations ?
A


B


C


D


Answer :


58. The general formula $${C_n}{H_{2n}}{O_2}$$ could be for open chain
A
carboxylic acids
B
diols
C
dialdehydes
D
diketones
Answer :
carboxylic acids
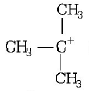
59. Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation?
A
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{+}{\mathop{-C-}}}\,H\]
B
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}} \\
|
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-{{C}^{+}}}}}\,\]
C
\[\overset{+\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}}}\,\]
D
\[\overset{\,\,\,\,\,+}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}}}\,\]
Answer :
\[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\begin{smallmatrix}
| \\
\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}
\end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix}
\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}} \\
|
\end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{-{{C}^{+}}}}}\,\]
60. The blue compound formed in the positive test for nitrogen with Lassaigne solution of an organic compound is
A
$$N{a_4}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_5}\left( {NOS} \right)} \right]$$
B
$$N{a_3}\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]$$
C
$$Fe{\left( {CN} \right)_3}$$
D
$$F{e_4}{\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]_3}$$
Answer :
$$F{e_4}{\left[ {Fe{{\left( {CN} \right)}_6}} \right]_3}$$








 shows nine resonating structures due to the presence of nine $$\alpha {\text{ - }}C - H$$ bonds.
shows nine resonating structures due to the presence of nine $$\alpha {\text{ - }}C - H$$ bonds.