Question
A pendulum is displaced to an angle $$\theta $$ from its equilibrium position, then it will pass through its mean position with a velocity $$v$$ equal to
A.
$$\sqrt {2gl} $$
B.
$$\sqrt {2gl\sin \theta } $$
C.
$$\sqrt {2gl\cos \theta } $$
D.
$$\sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} $$
Answer :
$$\sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} $$
Solution :
If $$l$$ is the length of pendulum and $$\theta $$ the angular amplitude, then height
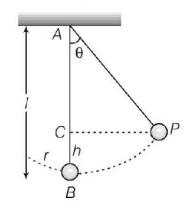
$$\eqalign{ & h = AB - AC \cr & = l - l\cos \theta \cr & = l\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\,......\left( {\text{i}} \right) \cr} $$
At point $$P$$ (maximum displacement position i.e. extreme position), potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. At point $$B$$ (mean or equilibrium position) potential energy is minimum and kinetic energy is maximum, so from principle of conservation of energy.
$$\eqalign{ & \left( {PE + KE} \right)\,{\text{at}}\,P = \left( {KE + PE} \right)\,{\text{at}}\,B \cr & {\text{or}}\,\,mgh + 0 = \frac{1}{2}m{v^2} + 0 \cr & {\text{or}}\,\,v = \sqrt {2gh} \,......\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right) \cr} $$
Substituting the value of $$h$$ from Eq. (i) into Eq. (ii),
$$v = \sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} $$
If $$l$$ is the length of pendulum and $$\theta $$ the angular amplitude, then height

$$\eqalign{ & h = AB - AC \cr & = l - l\cos \theta \cr & = l\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\,......\left( {\text{i}} \right) \cr} $$
At point $$P$$ (maximum displacement position i.e. extreme position), potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. At point $$B$$ (mean or equilibrium position) potential energy is minimum and kinetic energy is maximum, so from principle of conservation of energy.
$$\eqalign{ & \left( {PE + KE} \right)\,{\text{at}}\,P = \left( {KE + PE} \right)\,{\text{at}}\,B \cr & {\text{or}}\,\,mgh + 0 = \frac{1}{2}m{v^2} + 0 \cr & {\text{or}}\,\,v = \sqrt {2gh} \,......\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right) \cr} $$
Substituting the value of $$h$$ from Eq. (i) into Eq. (ii),
$$v = \sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} $$