Question
A long straight wire of radius $$a$$ carries a steady current $$i.$$ The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. The ratio of the magnetic field at $$\frac{a}{2}$$ and $$2a$$ is
A.
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
B.
$$\frac{1}{4}$$
C.
4
D.
1
Answer :
1
Solution :
Here, current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section of the wire, therefore, current enclosed in the amperean path formed at a distance $${r_1}\left( { = \frac{a}{2}} \right) = \left( {\frac{{\pi r_1^2}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) \times I,$$ where $$I$$ is total current
∴ Magnetic field at $${P_1}$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & {B_1} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times {\text{current enclosed}}}}{{{\text{Path}}}} \cr & \Rightarrow {B_1} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times \left( {\frac{{\pi r_1^2}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) \times I}}{{2\pi {r_1}}} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times I{r_1}}}{{2\pi {a^2}}} \cr} $$
Now, magnetic field at point $${P_2},$$
$${B_2} = \frac{{{\mu _0}}}{{2\pi }}.\frac{I}{{\left( {2a} \right)}} = \frac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi {a^2}}}.$$
∴ Required ratio = $$\frac{{{B_1}}}{{{B_2}}} = \frac{{{\mu _0}I{r_1}}}{{2\pi {a^2}}} \times \frac{{4\pi a}}{{{\mu _0}I}}$$
$$ = \frac{{2{r_1}}}{a} = \frac{{2 \times \frac{a}{2}}}{a} = 1.$$
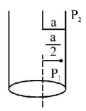
Here, current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section of the wire, therefore, current enclosed in the amperean path formed at a distance $${r_1}\left( { = \frac{a}{2}} \right) = \left( {\frac{{\pi r_1^2}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) \times I,$$ where $$I$$ is total current
∴ Magnetic field at $${P_1}$$ is
$$\eqalign{ & {B_1} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times {\text{current enclosed}}}}{{{\text{Path}}}} \cr & \Rightarrow {B_1} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times \left( {\frac{{\pi r_1^2}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) \times I}}{{2\pi {r_1}}} = \frac{{{\mu _0} \times I{r_1}}}{{2\pi {a^2}}} \cr} $$
Now, magnetic field at point $${P_2},$$
$${B_2} = \frac{{{\mu _0}}}{{2\pi }}.\frac{I}{{\left( {2a} \right)}} = \frac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi {a^2}}}.$$
∴ Required ratio = $$\frac{{{B_1}}}{{{B_2}}} = \frac{{{\mu _0}I{r_1}}}{{2\pi {a^2}}} \times \frac{{4\pi a}}{{{\mu _0}I}}$$
$$ = \frac{{2{r_1}}}{a} = \frac{{2 \times \frac{a}{2}}}{a} = 1.$$
