Question
A coil in the shape of an equilateral triangle of side $$l$$ is suspended between the pole pieces of a permanent magnet such that $$B$$ is in plane of the coil. If due to a current $$i$$ in the triangle a torque $$\tau $$ acts on it, the side $$l$$ of the triangle is
A.
$$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\left( {\frac{\tau }{{Bi}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
B.
$$\frac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}\left( {\frac{\tau }{{Bi}}} \right)$$
C.
$$2{\left( {\frac{\tau }{{\sqrt 3 Bi}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
D.
$$\frac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\frac{\tau }{{Bi}}$$
Answer :
$$2{\left( {\frac{\tau }{{\sqrt 3 Bi}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
Solution :
Torque acting on equilateral triangle in a magnetic field $$B$$ is
$$\tau = M \times B,\tau = iAB\sin \theta \,\,\,\left[ {iA = M} \right]$$
Area of $$\Delta LMN$$
$$A = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{l^2}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,\theta = {90^ \circ }\,\,\left[ {l = {\text{sides of triangle}}} \right]$$
Substituting the given values in the expression for torque, we have
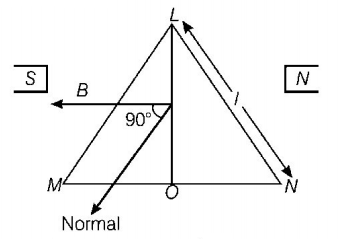
$$\tau = i \times \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{l^2}B\sin {90^ \circ } = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}i{l^2}B\,\,\left( {\because \sin {{90}^ \circ } = 1} \right)$$
Hence, $$l = 2{\left( {\frac{\tau }{{\sqrt 3 Bi}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$
Torque acting on equilateral triangle in a magnetic field $$B$$ is
$$\tau = M \times B,\tau = iAB\sin \theta \,\,\,\left[ {iA = M} \right]$$
Area of $$\Delta LMN$$
$$A = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{l^2}\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,\theta = {90^ \circ }\,\,\left[ {l = {\text{sides of triangle}}} \right]$$
Substituting the given values in the expression for torque, we have

$$\tau = i \times \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{l^2}B\sin {90^ \circ } = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}i{l^2}B\,\,\left( {\because \sin {{90}^ \circ } = 1} \right)$$
Hence, $$l = 2{\left( {\frac{\tau }{{\sqrt 3 Bi}}} \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}}$$